Mashina ( lat. Machina - “device, construction”, from other Greek. Μηχανή - “device, method”) - a technical device that performs mechanical movements to convert energy , materials and information [1] . In a more expanded modern definition that appeared with the development of electronics , a machine is a technical object, consisting of interconnected functional parts (parts, assemblies, devices, mechanisms , etc.) that use energy to perform the functions assigned to it [2] . In this sense, the machine may not contain mechanically moving parts. An example of such devices is an electronic computer ( computer ), an electric transformer , an accelerator of charged particles .
Machines are used to perform certain actions in order to reduce the load on a person or completely replace a person in a specific task. They are the main means to increase labor productivity .

A simple machine is a mechanism that changes direction or magnitude of a force without consuming energy.
History

A number of simple machines ( lever , wheel, block ) have been known since prehistoric times.
The first known prototype of a complex machine, as a device for converting energy from one type to another, was a water- filled water wheel ; from ancient times, the ancient Egyptians and Persians used it for irrigation. This mechanical device was used to convert the energy of falling water ( hydropower ) into the energy of rotational motion.
In the era of antiquity, machines as mechanical devices were used to enhance human capabilities for one point: lifting blocks , a lever , wheel carts , a dough mixing machine, screw press , auger ( Archimedes screw ). Machines were also considered simple scaffolding . The prototypes of more complex machines as ingenious devices served to entertain the public, such as the Heron steam engine.
In the days of the Roman Empire, the design of machines was an architecture and applied. [4] The main efforts of the engineers were aimed at improving military equipment and hand tools , throwing tools , devices for sawing stone blocks.
In the era of the late Roman Empire and the medieval West, the word "machine" was applied only to siege weapons .
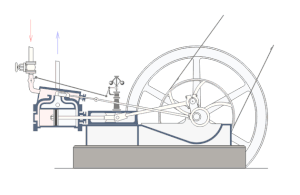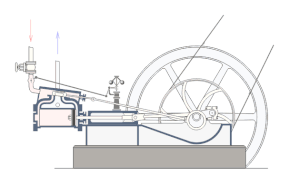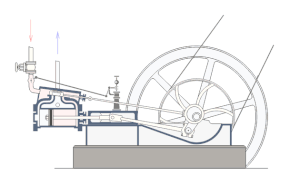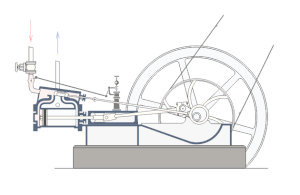
The creation of the universal steam engine in 1774 by James Watt marked the beginning of the technological revolution and the ever-accelerating technological progress. Complex equipment and propulsion systems appear, such as the steam turbine invented in 1889 by Gustaf de Laval , in 1870-1890 an internal combustion engine (gas - Nikolaus Otto , gas - Gottlieb Daimler and Karl Benz , diesel - Rudolf Diesel ), in 1889 year, Mikhail Dolivo-Dobrovolsky - AC electric motor.
The functioning of new machines begins to widely use the phenomena of mechanics, thermodynamics, electromagnetism. Technical objects become physically complex. To designate certain types of technical devices, the terms “ apparatus ”, “ instrument ” are introduced.
Historically, a machine has been classified as a device containing moving parts and used to convert mechanical energy. However, with the advent and development of electronics , machines without moving parts appeared.
Device and components
The basis of a mechanical machine is mechanisms (for example, a crank mechanism as part of a steam engine ). Externally, different machines may contain similar or similar mechanisms. But the most important components remain invariable always, in all machines, such as: engine, moving parts, etc.
The machine consists of an engine as a source of energy (movement), transmission and executive devices, and a control system . Together, the first three parts are usually called a machine assembly . A mechanical transmission device is called a transmission mechanism , and a mechanical actuator is called an actuator .
In machines, either the engine or the actuator (or both, together) perform mechanical movements. The rest of the machine can be based on other principles of action (for example, use the laws of optics, electrodynamics, etc.).
The part of the machine unit, including the engine and the transmission device, is the drive . The machines use mechanical as well as combined drives - electromechanical, optomechanical, hydroelectromechanical, etc.
The engine and / or actuator of the machine perform a given function, making certain movements - for example, moving the pump piston, robot arms. The design of such devices is to create mechanisms that provide, first of all, the given form and law of motion. These problems are solved by methods of the theory of mechanisms and machines .
The main characteristic of a machine engine is the power it develops. One of the first units of power measurement was horsepower (hp). Despite the fact that the Russian Federation has adopted the International System of Units (SI) and the unit of measure for power is watt , horsepower continues to be used today.
A mechanical transmission device (transmission mechanism) is designed to transmit mechanical energy. It is necessary to coordinate the relative position and motion parameters of the engine and actuator. This, in turn, allows you to subdivide transmission devices into the following:
- transmissions - only transmit the movement from the remote engine to the actuator without changing the characteristics of this movement. For example, from a car engine located in its front end to the rear wheels (drive axle);
- transmission - coordinate the parameters and type of movement at the engine output with the input characteristics of the actuator. Mechanical gears that slow down the transmitted movement are classified as gearboxes , and accelerating gears as multipliers .
Machine Classification
By appointment
Almost any car can be attributed to one of the following three groups:
- Energy machines are machines that transform one form of energy into another. These include:
- engines - machines that turn various types of energy into mechanical work ( electric motors , steam engines , hydraulic turbines , internal combustion engines );
- generators - machines that convert mechanical energy into any other type of energy ( electric generators , reciprocating compressors, pump mechanisms).
- Working machines are machines that use mechanical or other energy to transform and move workpieces and loads. These include:
- technological machines and apparatuses - mills , furnaces, machine tools , presses , etc., which are designed to change the size, shape, properties or condition of the subject of processing (raw materials).
- transport and lifting machines - cars , cable cars , conveyors , cranes, elevators, airplanes, etc. devices that are designed to move workpieces, goods and people in space.
- Information machines are machines that are designed to convert, process and transmit information (various mechanical and electronic controllers, computers , musical instruments , communication devices and other devices for transmitting, processing and storing information).
The development trend of modern machines is the creation of combined machines - machine aggregates. A machine unit is a technical system consisting of one or more standardized units connected in series or in parallel and designed to perform certain useful functions. Typically, a machine assembly includes: an engine , a transmission mechanism (there may be several or not at all), and a working or power machine . Currently, the machine often includes an information machine.
The use of information machines to control energy and working machines has led to the emergence of cybernetic machines that can adapt to environmental changes through the use of artificial intelligence systems : (robots , manipulators, automatic machines and flexible production systems). The combination of different working machines in one design led to the appearance of combine machines, and the combination of different energy machines gave impetus to the development of hybrid designs.
By degree of versatility
By the degree of universality, machines are divided into three groups: universal, specialized, and special.
- Universal machines are designed to carry out diverse technological and transport operations related to the processing and processing of various items of processing, energy or information flows. This is the most common group of machines, which include universal metal-cutting machines, forging machines, transport and transportation machines. The list of operations or work that is performed by a universal machine is quite wide. Machines that are used to perform a very wide range of work are called universal. This also includes personal computers , whose functions depend on the type of software that is currently running on them.
- Specialized machines are designed for processing or processing objects of the same nomenclature, which differ in shape, size or properties (gear-cutting or thread-cutting machines, blast furnaces , milling equipment, agricultural machines, printing machines, etc.). This group includes programmable logic controllers whose functions are limited by the range of control tasks for which they are created.
- Special machines are designed to process or process objects of labor only of a certain shape, size or properties, as well as to perform any specific work or operation. This can be machines for processing, for example, gas turbine blades , cars for transporting only a certain type of cargo ( cement trucks , fuel trucks , panel trucks), etc. Here you can also recall electronic devices (measuring, household, communications, etc.) , built on single-chip computers, where exactly those functions that are inherent and necessary for this device are laid out in circuit and software.
By degree of automation
By the degree of automation, all machines are divided into manual machines, automatic machines and semi-automatic machines.
- Manual machines perform their functions only with the direct participation of a person in their work. A person starts a machine, controls the operation of all its mechanisms and stops the machine after performing certain work or operations (metal-cutting and woodworking machines, construction machines, transport and transporting machines, sewing machines , etc.).
- An automaton is an independently operating machine that performs its function according to a given control program without direct human participation in the processing, transformation, transmission and use of material objects, energy or information. There are technological automatic machines (for example, metal-cutting automatic machines, foundry machines, automated units, etc.), power machines (automatic devices and means of power systems, electric machines and networks), transport ( automatic stop , autopilot ), computing machines, and trading (automatic cooking machine, automatic machine), household machines. Depending on the working conditions and the type of energy used, there are machines that include mechanical, hydraulic, electrical (electronic), pneumatic and combined devices.
- Automated devices (semiautomatic devices) are machines in which the duty cycle, which is carried out on the basis of a predetermined control program, is interrupted and for its repetition, mandatory human intervention (coffee machine, microwave oven , etc.) is necessary.
General characteristics of the machines
A machine meets its purpose only if it is characterized by the following required characteristics:
- productivity - the higher it is, the lower the cost of production;
- profitability - the machine should have a large efficiency , take up less space , spend less energy, fuel , provide higher accuracy, require less labor for maintenance and repair, etc. All this can be achieved by improving the design of the machine, rational selection of its main parameters and structural forms, using automatic systems for regulating and controlling the machine and ensuring optimization of the operating mode .;
- operational reliability - the property of a machine to perform specified functions, while maintaining its operational performance within acceptable limits, for a predetermined period of time. Reliability indicator can be the probability of machine failure-free operation in the designated time interval with minimal repair costs. The closer to unity the probability of failure-free operation, the higher the reliability of the machine;
- durability - the ability of the machine and its components to withstand the effects of aging, wear, corrosion , etc. It determines the condition of the machine in which it is able to perform specified functions with parameters according to the requirements of technical documentation while maintaining strength , shape and size, stability against operation, necessary mechanical rigidity, heat and vibration resistance. The operability of machine parts is ensured by giving them appropriate sizes and shapes, a rational selection of materials for their manufacture using reinforcing technologies, the use of corrosion protection and appropriate lubrication;
- manufacturability of the design - the degree to which the design of the machine matches the optimal production conditions for a given scale of production;
- environmental friendliness of the machine - its ability to perform its functions without harmful effects on the environment or with minimizing such impact. Environmental friendliness is ensured when designing and constructing a machine using technologically clean energy sources, preventing harmful pollution of industrial premises, neutralizing machine workflow products, properly sealing its working volumes, using materials for parts, taking into account the possibility of disposal after failure, and ensuring that the machine functions as low noise and vibration levels.
- безопасность в эксплуатации характеризует пригодность конструкции машины к нормальной эксплуатации в течение определённого технической документацией срока службы без аварийных разрушений, опасных для обслуживающего персонала, производственного оборудования, а также других смежных объектов.
- стоимость — зависит в первую очередь от массы машины; чем она меньше, тем больше экономия металлов и других материалов и тем ниже стоимость машины. На стоимость влияет и много других факторов, таких как степень совершенства технологического процесса производства, степень унификации конструкции машины, стоимость материалов и покупных изделий, необходимых для её изготовления и т. д.
Прежде всего машина должна полностью соответствовать требованиям и нормам конструкторской документации, технических условий и стандартов.
Функциональная структура машин
По функциональными признакам в структуру машины входят взаимосвязанные механизмы , на каждый из которых возложена определённая функция. Механизмы могут состоять из твёрдых тел , содержать гидравлические , пневматические, электрические компоненты, работа которых базируется на использовании жидких, газообразных тел или электрического тока соответственно.
C точки зрения функционального назначения механизмы машин делятся на следующие виды:
- механизмы двигателей и преобразователей ( турбины , генераторы , насосы и т. д.);
- передаточные механизмы ( редукторы , ремённые передачи , цепные передачи и т. д.);
- исполнительные механизмы (механизмы прессов , механизмы перемещения инструмента, механизм ковша экскаватора и т. д.);
- средства управления, контроля и регулировки ( датчики , действие которых основано на изменении электрического сопротивления , ёмкости , индуктивности , а также на возникновении электродвижущей силы в процессе действия контролируемых механических, акустических , тепловых, электрических, магнитных, оптических или радиационных величин; программируемые логические контроллеры , системы ЧПУ и др.);
- средства подачи, транспортировки, питания и сортировки (механизмы винтовых шнеков, скребковых и ковшовых элеваторов, для транспортировки и подачи сыпучих материалов, механизмы сортировки готовой продукции по размерам, форме, виду и т. д.);
- средства автоматического учёта, дозировки и упаковки готовой продукции (механизмы дозировки и упаковки пищевых продуктов, механизмы дозировки и розлива продукции в виде жидкости и т. д.).
В зависимости от назначения, конструкции и принципа работы конкретной машины в её состав могут входить несколько механизмов одинакового назначения (например, механизмов двигателей или насосов, передающих или исполнительных механизмов) или некоторые из рассмотренных видов механизмов могут отсутствовать. Рабочая машина чаще всего состоит из трёх основных механизмов: двигателя, трансмиссии и исполнительного, или собственно рабочего механизма, которым определятся специализация машины и ради которого машина и создаётся (металлообрабатывающая машина, зерноуборочный комбайн и т. д.).
Конструктивная структура
Конструктивно машина состоит из деталей, узлов и агрегатов . Каждый из этих элементов имеет предметную или функциональную специализацию, полное назначение и вместе с тем согласуется с другими элементами машины, образуя в совокупности целостную действующую конструкцию.
Детали машин
Деталь — элемент машины, представляющий собой одно целое, который не может быть разобран без разрушения на более простые составляющие части. Количество деталей в современных машинах достигает десятков тысяч. Выполнение машин из деталей прежде всего вызвано необходимостью обеспечения относительных движений (степеней свободы) её частей. Но неподвижные и взаимно неподвижные части машин (звенья) также выполняют из отдельных соединённых деталей. Это даёт возможность применять оптимальные материалы, быстро восстанавливать работоспособность изношенных машин, заменяя только простые и изношенные детали, что облегчает их изготовление, обеспечивает возможность и удобство процесса сборки машин.
По признакам применения и распространённости в машиностроении детали можно разделить на группы:
- стандартные — это детали, изготавливаемые в соответствии с государственными, отраслевыми стандартами или стандартами предприятия;
- унифицированные — это детали, заимствованные из другого изделия, то есть ранее спроектированные как оригинальные;
- оригинальные — детали конструируют для определённой машины и они, как правило, раньше не проектировались и не изготавливались.
Узлы машин
Узел — часть машины, представляющая собой разъёмное или неразъёмное соединение нескольких деталей, которое можно собрать отдельно от других составных частей машины или механизма и которое способно выполнять определённые функции в изделиях одного назначения только совместно с другими составными частями. Особенностью каждого конкретного узла является то, что он может выполнять свои функции только в составе определённой машины, для которой он предназначен. Характерными примерами узлов могут быть сварные корпуса, гидро- и пневмоцилиндры, планетарные механизмы, тормозные устройства, шпиндельные блоки, обгонные муфты, предохранительные клапаны и др.
Агрегаты
Агрегат — нормализованный узел машины, который обеспечивает полную взаимозаменяемость и самостоятельно выполняет свойственные ему функции. Это даёт возможность использовать агрегаты не только в конструкции какой-то определённой машины, а составлять из них, в зависимости от потребностей производства, машины разных компоновок (машинные агрегаты). Так, например, в машиностроительном производстве получили широкое использование агрегатные станки, в состав которых входят только нормализованные элементы (агрегаты) в виде силовых столов, многопозиционных поворотных столов, силовых головок, шпиндельных коробок и гидропанелей. Благодаря стандартизированным соединительным размерам из этих элементов могут компоноваться агрегатные станки различного назначения.
Типичными образцами агрегатов, входящих в состав машин, являются электрические двигатели , редукторы, насосы, различного назначения, гидроагрегаты в виде гидроусилителей, генераторы электрического тока , компрессоры и многие другие. Из агрегатов компонуют некоторые машины сельскохозяйственного производства; большое количество агрегатов входит в состав машиностроительной , транспортной и транспортирующей техники, машин химической и перерабатывающей промышленности, прокатных станов металлургического производства .
Особенности взаимодействия в системе «человек-машина»
Under the “man-machine” system is meant a system that includes a human operator (a group of operators) and a machine through which labor is carried out. The “man-machine” system is a special case of control systems in which the functioning of the machine and human activity are connected by a single control loop. In organizing the relationship between man and machine, the main role belongs not so much to the anatomical and physiological as to the psychological properties of a person: perception, memory , thinking , attention , etc. His informational interaction with the machine largely depends on the psychological properties of a person. Features of this interaction is the object of study of engineering psychology, the general theory of systems and its applied direction, systems engineering.
Under the system in the general theory of systems is understood a complex of interconnected and interacting elements, designed to solve a single problem. Systems can be classified according to various criteria. One of them may be the degree of human participation in the system.
From this point of view, automatic, automated and non-automatic systems are distinguished. The automatic system operates without human intervention. In non-automatic systems, control actions are carried out exclusively by a person, and both a person and technical devices take part in the work of an automated system. As a matter of fact, it is the latter systems that are human-machine systems.
In practice, the most diverse types of human-machine systems are used. The basis of their classification can be the following four groups of signs:
- the purpose of the system is management, maintenance, training, information, research. A feature of control and maintenance systems is that the object of targeted actions in them is the machine component of the system. In educational and information systems, the direction of the effects is the opposite - on the person. In research systems, exposure has both directions;
- characteristics of the human link - a monosystem, when a machine or a system of machines interacts with one person, and a polysystem, when a collective of people is involved in the management;
- type and structure of the machine link - according to the degree of complexity of the functions performed, it is possible to distinguish simple machines (tools, energy converters, etc.), complex machines (rolling mills, power equipment, automated lines) and systems complexes (air liner, industrial enterprise, computer center , transport system, etc.);
- type of interaction of system components - can be continuous and episodic (regular or stochastic).
Scientific Basics
The scientific basis for the development and operation of machines is machine science - a branch of science and technology that is engaged in the design, calculations, methods and means of experimental determination of an elastically deformed state; testing, manufacturing, operation and repair of parts, assemblies, individual mechanisms and machines in general; the creation of rational designs, increased efficiency, reliability and durability of machine parts; the development of new and improvement of existing technical and design solutions that provide improved quality and operational efficiency, regardless of the field of technology and the purpose of the machines.
General problems of machine science
Common problems in machine science include:
- development of principles for the creation of machines, methods of calculation and design of parts and components of machines;
- system analysis of structures and generalization of engineering experience in machine design;
- finding ways to increase the specific performance of machines, improving existing designs in order to increase efficiency and reduce the weight of machines.
Applied Problems of Mechanical Engineering
The applied problems of engineering include:
- carrying out structural, kinematic and dynamic analysis of schemes of mechanisms and machines;
- increase of working capacity, reliability and durability of mechanisms and machines.
- development of the theory and methods of optimal synthesis of mechanisms and machine assemblies according to given working conditions.
- development of the theory of automatic machines;
- studies of the kinematics of mechanisms and machines, methods and means of loading their elements, measuring stresses, strains.
Calculation, design and testing of machines
In this area of machine science, actual problems are:
- study of the influence of materials, processing technology and operating conditions on the performance, reliability, durability of machines and mechanisms;
- testing and diagnostics of machine parts and components;
- development of methods and tools for diagnosing machines;
- development of methods and means of protecting machines from overload.
Other values
- The word car is often called a car .
- An abstract mathematical concept, a synonym for the concept of “automaton,” such as a Turing machine .
See also
- Car
- Deus ex machina ("God of the car")
- Goldberg Machine
- Dynamo machine
- Engineering
- Mechanism
- Steam engine
- Self propelled car
- Electric car
- Device
Notes
- ↑ Machine - an article from the Great Soviet Encyclopedia .
- ↑ The American Heritage Dictionary, Second College Edition. Houghton Mifflin Co., 1985.
- ↑ Chambers, Ephraim (1728), Table of Mechanicks , vol. Volume 2, London, England, p. 528, Plate 11 .
- ↑ Vitruvius. Ten books on architecture. - M .: publishing house of the All-Union Academy of Architecture, 1936. - 332 p.
Literature
- Artobolevsky I. I. Theory of mechanisms and machines: Textbook. for technical colleges. - 4th ed., Revised. and add. - M .: Nauka, 1988 .-- 640 p.
- Technique in its historical development. In 2 volumes. - M .: Science, 1979-1982.
- Khoroshev A.N. Introduction to the management of the design of mechanical systems: Textbook. - Belgorod, 1999 .-- 372 p. - ISBN 5-217-00016-3 . (electronic version 2011)
- Small mountain encyclopedia . In 3 t. = Mala gіrnicha encyclopedia / (In Ukrainian). Ed. V.S. Beletsky . - Donetsk: Donbass, 2004. - ISBN 966-7804-14-3 .
- Kіnitsky Ya. T. Theory of machinery and machines: A Textbook . - K .: Naukova Dumka, 2002 .-- 660 p. - ISBN 966-00-0740-X
- B. I. Krasny Theory of Mechanisms and Machines : Lecture course for students in the 0902 “Engineering Mechanics” field of study full-time and part-time. - Exactly: NUVHP, 2006 .-- 216 p.
- Sidorenko V.K., Tereshchuk G.V., Yurzhenko V.V. Fundamentals of engineering and technology: Textbook. - M .: NPU, 2001 .-- 163 s.
- Oberg, Erik; Franklin D. Jones, Holbrook L. Horton, and Henry H. Ryffel (2000). ed. Christopher J. McCauley, Riccardo Heald, and Muhammed Iqbal Hussain. ed. Machinery's Handbook (26th edition ed.). New York: Industrial Press Inc .. ISBN 0-8311-2635-3 .
- Sybille Krämer: Symbolische Maschinen. Die Idee der Formalisierung in geschichtlichem Abriss. Wissenschaftliche Buchgesellschaft, Darmstadt 1988, ISBN 3-534-03207-1
- Hans-Dieter Bahr: Über den Umgang mit Maschinen. Konkursbuchverlag, Tübingen 1983, ISBN 3-88769-011-7
- Martin Burckhardt: Vom Geist der Maschine. Eine Geschichte kultureller Umbrüche. Campus Verlag, Frankfurt / M. / New York 1999, ISBN 3-593-36275-9