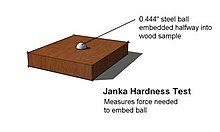
The Yank hardness test is used to assess the hardness of wood . It is expressed in force in pounds , which must be applied to a metal ball with a diameter of 0.444 inches (11.28 millimeters ) to press it into the wood by half the diameter.
The hardness test was invented by the Austrian Gabriel Janka ( German: Gabriel Janka , 1864-1932), who investigated the problems of elasticity and hardness of different types of wood .
The complexity of wood processing is not always directly proportional to the Yank scale. For example, oily wood with a high hardness index is much easier to process than less hard dry wood.
Values for some types of wood:
| Wood | Yank value (in pounds) |
|---|---|
| Allocasuarina luehmannii | 5060 |
| Guaiac tree | 4500 |
| Kurupi | 3880 |
| Ipe ( Tabebuia ) | 3640 |
| Red walnut | 2450 |
| Brazilian Cherry | 2350 |
| Mesquite tree | 2345 |
| Mahogany Sansus | 2200 |
| Merbau | 1925 |
| West Australian Eucalyptus | 1910 |
| Amaranth | 1860 |
| Australian walnut | 1820 |
| African paduc | 1725 |
| Brazilian nut | 1650 |
| Wenge | 1630 |
| Canadian Maple | 1450 |
| Bamboo | 1380 |
| White oak | 1360 |
| Ash | 1320 |
| American beech | 1300 |
| Red oak | 1290 |
| Yellow birch | 1260 |
| Teak | 1155 |
| Siberian larch | 1100 |
| Black walnut | 1010 |
| American cherry | 950 |
| Geoffrey Pine, Yellow Pine | 870 |
| Douglas fir | 660 |
| Balsa | 100 |
| Cavanillesia platanifolia | 22 |
See Also
List of wood species showing typical Yank hardness