Accumulator fuel system or system like " common rail " ( English common rail - common line) - a fuel supply system used in diesel engines . In a common rail system, a high-pressure pump pumps diesel fuel under high pressure (up to 300 MPa, depending on the engine's operating mode) into a substantial bulk fuel line (battery) [1] .


Electronics-controlled electro-hydraulic nozzles with an electromagnetic or piezoelectric control valve actuator inject diesel fuel under high pressure into the cylinders . Depending on the design of the injectors and the class of the engine, up to 9 servings of fuel per 1 cycle can be injected.
One of the key features of common rail systems is the independence of the injection processes from the angle of rotation of the crankshaft and the engine operating mode, which makes it possible to achieve high injection pressure in partial modes, which is necessary to meet modern and future environmental requirements.
Content
Design and Function
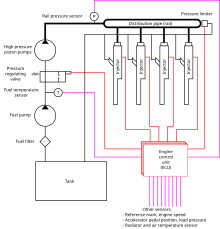
The fuel from the fuel tank is taken up by the fuel priming pump (low pressure), and through the fuel filter enters the high pressure fuel pump (high-pressure fuel pump). Injection pump supplies fuel to the pressure line, which plays the role of a pressure accumulator . The control unit controls the performance of the high-pressure fuel pump to maintain the necessary pressure in the line as fuel is consumed.
The fuel line is connected by fuel lines to the nozzles . A control valve is integrated in each nozzle - electromagnetic or piezoelectric . At the command of the control unit, the valve opens, injecting the necessary portion of fuel into the cylinder.
Comparison with other fuel supply systems
Features:
- Unlike the traditional fuel supply system, a single-channel fuel injection pump is used, which constantly supplies fuel to the highway;
- It is necessary to adjust the operation cycle based on the throughput of each nozzle, because of which it is necessary to configure the electronic unit after each nozzle replacement.
Benefits:
- The pressure at which the fuel is injected can be maintained regardless of the speed of the engine crankshaft and it remains almost constantly high during the entire fuel supply cycle, which is especially important for stabilizing combustion at idle and at low speeds when operating at partial load;
- When using a battery-powered fuel supply system, the timing of the start and end of the feed can be widely controlled by the computer. This allows you to more accurately meter the fuel, as well as to supply fuel in several portions during the working cycle - for a more complete combustion of fuel;
- The common rail design is simpler than the injection pump system with nozzles, its maintainability is higher.
Disadvantages:
- More sophisticated injectors that require relatively frequent replacement compared to a traditional fuel supply system;
- The system ceases to work during depressurization of any high-pressure element, for example, if one of the nozzles malfunctions when its valve is constantly in the open position;
- Higher fuel quality requirements than traditional systems.
Thus, to meet promising environmental standards, such as Euro-VI , Tier-IV, Euro Stage IV for heavy diesel engines, common rail systems were considered the most suitable for diesel engines of all classes.
System Media
Currently, up to 70% of all diesel engines manufactured are equipped with common rail systems, and this share is growing [2] . According to the forecasts of Robert Bosch GmbH, the share of the CR system in the market by 2016 will reach 83%, and in 2008 their number was only 24%. Thus, today almost every manufacturer of engines of all classes: from small passenger cars to large marine ones, has mastered the use of battery systems.
Among the manufacturers of fuel supply equipment and common rail systems in particular, the leaders are the following companies: R. Bosch , Denso, Delphi , L'Orange, Scania .
History
For the first time, a direct fuel injection system on diesel engines was developed and implemented in 1939 by Soviet engineers when creating an engine of the V-2 family at the Kharkov Locomotive Plant.
The prototype of the common rail system was created in the late 1960s by Robert Huber in Switzerland, then the technology was developed by Dr. Marko Ganser from the Swiss Higher Technical School of Zurich .
In the mid-1990s, Dr. Shohei Ito and Masahiko Miyaki of Denso Corporation developed the common rail system for commercial vehicles and implemented it in the ECD-U2 system, which was used on Hino Rising Ranger trucks; in 1995, they sold the technology to other manufacturers. Denso is therefore considered a pioneer in adapting the common rail system to the needs of the automotive industry.
Modern common rail systems operate on the same principle. They are controlled by an electronic control unit that opens each injector electronically, not mechanically. This technology was developed in detail by the joint efforts of Magneti Marelli , Centro Ricerche Fiat and Elasis. After Fiat developed the design and concept of the system, it was sold to the German company Robert Bosch GmbH to develop a mass product. This turned out to be a big miscalculation of Fiat, as the new technology became very profitable, but at that time the Italian group did not have the financial resources to complete the work. However, Italians were the first to use the common rail system in 1997 on the Alfa Romeo 156 1.9 JTD and only then it appeared on the Mercedes-Benz C 220 CDI .
Interesting Facts
- The development of battery power systems was carried out as early as the middle of the 20th century in the USSR at the Kolomensky Zavod , however, due to the insufficient development of electronics in those days, there were no successful implementations of such systems [3] .
- Currently, the vast majority of diesel engine manufacturers use common rail equipment due to the fact that previous generations of fuel equipment are not able to meet modern stringent environmental requirements.
- In the years 1934-35. was designed, and in 1936 was shown at the air show in Paris, the diesel engine Coatalen ( L. Coatalen ). The difference between the Coatalen diesel engine and other diesel engines was the injection of fuel into the cylinders not by hydraulic opening of the nozzle valve, but by mechanical opening and the use of a hydraulic accumulator, the fuel into which is pumped independently of the injection pump distribution system. In fact, a workable engine was shown on which the common rail system prototype was used. Louis Coatalen overtook the time by 60 years with such a fuel injection system [4] [5] [6] .
Notes
- ↑ Grekhov L.V., Ivashchenko N.A., Markov V.A. Fuel equipment and diesel control systems: Textbook for high schools. - M .: Legion-Avtodata, 2004 .-- 344 p. - 2500 copies. - ISBN 588850187-5 .
- ↑ Large Engine Injection Systems for Future. Christoph Kendlbacher, Peter Mueller, Martin Bernhaupt, Gerhard Rehbichler. Bergen: CIMAC, 2010. Full paper # 50.
- ↑ A.D. Blinov, P.A. Golubev, and others. Ed. V.S. Papanova and A.M. Mineeva. Modern approaches to the creation of diesel engines for cars and light trucks. - M .: SIC, 2000 .-- S. 124. - 332 p. - ISBN 5-8208-0027-3 .
- ↑ Melkumov T.M. , Aviation diesel engines . Moscow, 1940, pp .98-205
- ↑ http://www.oldengine.org/members/diesel/Duxford/aviat7.htm
- ↑ Chronology of Inventions of Tanks Page 29 - Guns.ru Talks