The Ten Years' War ( Spanish: Guerra de los Diez Años ), in Spain it is better known as the Cuban War ( Spanish) Guerra de Cuba , while in Cuba it is sometimes referred to as the Great War ( Spanish ( Guerra Grande ) or War 68 -th ( Spanish: Guerra del 68 ) - the first of three wars for the independence of Cuba from Spain . It began on October 10, 1868 , when the sugar industrialist Carlos Manuel de Cespedes and his supporters proclaimed Cuban independence from Spain, and continued until 1878 . The war ended in the defeat of the supporters of independence. It was followed by the Small War ( 1879 - 1880 ) and the War of Independence of Cuba ( 1895 - 1898 ), which passed into the Spanish-American War .
| Ten year war | |||
|---|---|---|---|
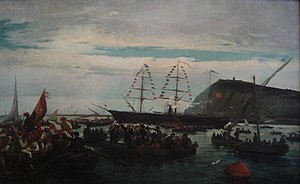 Spanish volunteers in the port of Barcelona board a ship to be sent to Cuba, 1870. | |||
| date | October 10, 1868 - February 10, 1878 | ||
| A place | Cuba | ||
| Total | The victory of Spain. Zanhon treaty . | ||
| Opponents | |||
| |||
| Commanders | |||
| |||
| Forces of the parties | |||
| |||
| Losses | |||
| |||
Content
Background
In 1857 - 1866, Cuba was in an economic crisis. The less economically developed eastern part of the island was particularly affected. The Spanish colonial administration continued to receive high incomes despite the crisis, but did not invest in the island's economy, but spent on military expenses (44%), government expenses (41%) and sent large amounts (12%) to Spain and Fernando- Po ( Spanish Guinea ). The Spaniards made up 8% of the population of Cuba and owned 90% of the island’s wealth. Spain established strict control over Cuban trade, which only exacerbated the effects of the crisis. The slave trade existed, and the island's economy depended on it substantially. The majority of the population of Cuba did not have any political rights and freedoms, in particular, they did not have the right to occupy any political posts, which led to the creation of clandestine organizations. Political parties were illegal. In addition, in 1868, a revolution took place in Spain, stimulating anti-colonial and anti-slavery movements in Cuba. In 1865, the Dominican Republic gained independence from Spain for the second time, and this event received a huge response in Cuba.
In July 1867, the Bayamo Revolutionary Committee was founded, headed by one of the island’s richest planters, Francisco Vicente Aguilera . The plot quickly spread throughout eastern Cuba, and in Manzanillo it entered the owner of the sugar plantation and sugar factory Carlos Manuel de Cespedes , who later became a key figure in the war. Authorities who were aware of Cespedes’s anti-colonial sentiment tried to persuade him to cooperate by arresting his son Oscar. Cespedes refused to negotiate, and his son was executed.
The course of the war
The war began on the morning of October 10, 1868 , when Carlos Manuel de Cespedes freed his slaves and wrote the Declaration of Independence (also known as the “October 10 Manifesto”). In independent Cuba, this day is celebrated as a national holiday, known as " Grito de Yara ."
As the first military action, Cespedes attacked the neighboring city of Yara on October 11 , but was brutally defeated. He managed to escape with only 12 allies. However, the rebellion after that received support in eastern Cuba. Already on October 13, the rebels took eight cities, and by the end of October 12 thousand people had joined it. Maximo Gomez , a former cavalryman of the Spanish army who served in the Dominican Republic, trained the rebel tactics of machete combat, which was constantly used in the war.
In October, the rebels took the large city of Bayamo , which caused a rise in feelings. The poet Pedro Figueredo wrote the national anthem of Cuba , Bayamo. A national government was formed, led by Cespedes. On January 12, 1869, Spanish troops captured Bayamo, and as a result the city was completely destroyed.
The war developed in the east of the island. So, on November 4, 1868, Camaguey was taken. The western provinces, Pinar del Rio , Havana , Matanzas , with rare exceptions, did not participate in the war. After a series of defeats, Cespedes replaced Gomez at the head of the army with American General Thomas Jordan . The latter used regular tactics, but it turned out that, although quite effective, it leaves the rebel families defenseless in the face of the Spanish troops. Then Gomez again led the command of the army.
On April 10, 1869, the Constitutional Assembly was held in Camaguey , in which representatives of areas controlled by the rebels took part. It was decided that civilian power should be separated from the military command. Carlos Manuel de Cespedes was elected president of the meeting, and the authors of the proposed Constitution, General Ignacio Agramonte y Loinas and Antonio Sambrana , as secretaries. After the meeting was completed, the House of Representatives began to work in the city, declaring itself the supreme power of Cuba. Salvador Cisneros Betancourt was elected its chairman. April 12, Cespedes was elected president of Cuba, General Manuel de Quesada - the commander of the armed forces.
After the colonial authorities could not agree with the rebels, at the beginning of 1869 they began a war of extermination. Laws were passed by which the leaders of the uprising and their accomplices could be executed on the spot; ships with weapons were detained, and all those on board were executed; men over 15 years old, detained outside their place of residence without supporting documents, could be executed on the spot, women were exiled to cities; cities that refuse to surrender to the Spanish army must be destroyed. In one episode, eight students from the University of Havana were shot on November 27, 1871 . In another, 53 people were shot after the detention of the Virginius ship on October 31, 1873 in extraterritorial waters.
Ignacio Agramonte was killed in battle on May 11, 1873 . After that, the Assembly, which already had a number of disagreements with Cespedes, ousted him from the post of president, replacing Salvador Cisneros. Cespedes himself was later captured and executed on February 27, 1874 , after the Cuban government refused his request to leave for the United States, where he intended to mobilize troops to help the rebels.
After 1873, the actions of the rebels were limited to the Camaguey and Oriente regions. In 1875, Gomez launched an invasion of Western Cuba, but did not receive support there, and in 1876 was forced to cease hostilities there. At the same time, after the end of the Spanish Civil War in 1876, new troops arrived from Spain to Cuba, the number of Spanish troops was increased to 250 thousand. Neither side was able to secure an immediate victory in the war, but Spain's prospects were clearly better.
End of War
Thomas Estrada Palma , the future first president of independent Cuba, replaced Cisneros as president. On October 19, 1877, he was captured by Spanish troops. On February 8, 1878, the Cuban authorities were dissolved and negotiations began with the colonial authorities in Zanhon. February 10, 1878 the parties signed the Zanhon Treaty . The war was formally ended on May 28, 1878 , after parts of the rebels in Los Mangos de Baragua , led by Antonio Maseo , ceased resistance because of its meaninglessness. Many war veterans became central figures in the next two wars for Cuban independence.
The Zanhon Treaty introduced reforms on the island, the purpose of which was to improve the financial situation of Cuba. All slaves who fought against Spain were freed. After this, slavery was doomed, and it was finally abolished by law in 1880 . Slaves had to work for their former masters for some time, but the masters were obliged to pay for labor.
Presumably, about 200 thousand people died during the war. The economy of the island has suffered significant damage.
International Reaction
The struggle of the Cubans aroused sympathy among the populations of other countries. El Salvador and Guatemala recognized Cuba as a belligerent [1] . A major international scandal was caused by the incident with the Virginius steamboat, which, under the American flag, was carrying a load of weapons and Cuban patriots to the rebels. The ship was detained in November 1873 in neutral waters off the coast of Jamaica by a Spanish warship. Although they managed to throw the cargo into the sea, the ship was escorted to Santiago de Cuba , where 53 people were shot after a military trial (crew members and passengers, including Cuban patriots, 16 British and Americans, including ship captain Joseph Fry) [2] . A great diplomatic scandal erupted between the United States, Spain and England. However, it was managed to be settled - in December 1873 the ship was returned, the surviving US citizens were released, and in 1875 the Spanish government agreed to pay $ 80,000 in compensation to the relatives of executed Americans [3] .
Literature
- José Cantón Navarro. History of Cuba, Havana, Cuba, 1998.
Notes
- ↑ Ivkina L.A. US policy towards Cuba during the war of independence (1867 - 1878) // Latin American historical almanac. - 2004. - No. 5. - S. 98
- ↑ Ivkina L.A. US policy towards Cuba during the war of independence (1867 - 1878) // Latin American historical almanac. - 2004. - No. 5. - S. 126
- ↑ Ivkina L.A. US policy towards Cuba during the war of independence (1867 - 1878) // Latin American historical almanac. - 2004. - No. 5. - P.127