
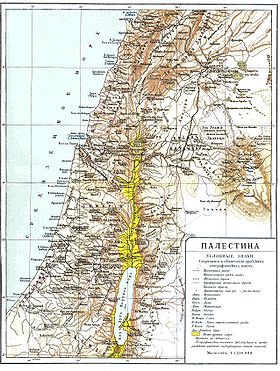
Palestine ( other Greek Παλαιστίνη , Palaistinê [1] from Aram. פלשת [2] - Pelešet , Hebrew ארץ פלשת - “Philistia”, lat. Palaestina [1] , Arabic. فلسطين - Falastin [3 ] ) Is a historical region in the Middle East . The borders of the region approximately cover the territory of the modern Gaza Strip , Israel , the Golan Heights , the West Bank , Jordan , parts of both Lebanon and Syria , from Sidon on the Mediterranean coast to Damascus in its northern part, and from Rafah to Aqaba Bay - south. The Sinai Peninsula , as a rule, is considered a separate geographical area [4] .
Content
- 1 Etymology of the name
- 2 Administrative Division of Palestine
- 3 Geography
- 4 History
- 4.1 Early history
- 4.2 Antiquity
- 4.3 The period of Arab rule (638-1099)
- 4.4 The period of the Crusaders (1099-1291)
- 4.5 Under the rule of the Ottoman Empire (1516-1917)
- 4.6 British Mandate
- 4.7 Subsequent Events
- 4.7.1 Creation of Israel
- 4.7.2 The struggle to create an Arab state in the 1960s – 2010s
- 5 Dispute over the historical right to Palestine
- 6 Russian presence in Palestine
- 7 notes
- 8 Literature
- 9 References
Name Etymology
The name “Palestine” comes from “Philistia” ( Hebrew ארץ פלשת , [ Eretz-P (e) leshet ]) - the name of the Philistines populated in ancient times [5] ( Hebrew פלישתים , plishtim , literally “invading” ») Parts of the Mediterranean coast of present-day Israel [6] [2] .
In the Semitic Canaanite languages ( Phoenician , Hebrew ), this region, and the entire western part of the Fertile Crescent as a whole, was called "Knaan" ("Kenaan"), in the modern Russian tradition - " Canaan ". Canaan was conquered by Jewish tribes in the middle of the II millennium BC. e. The book of Jesus Navin 11:23 ( Heb. יְהוֹשֻׁעַ בִּן-נוּן , Yehoshua bin Nun ) refers to the name "Land of the Sons of Israel" ( Hebrew ארץ בני ישראל , Eretz Bnei Israel ).
Some Greek writers, beginning with Herodotus (according to Roman scribes), called this land Syria Palestinian, or Palestine. Others used the general name Syria or the qualifying Kelesiria . Also applied division into the internal regions - Judea and the coastal region, which was considered as part of Phenicia . [7] [8] [9] [10]
In 1 Samuel 13:19 (1 Samuel ( Heb. סֵפֶר שְׁמוּאֵל , Sefer Shmuel )) in the account of the wars of King Saul (approximately 1030 BC), the name “ Land of Israel ” is first mentioned ( Hebrew ישראל ארץ , Eretz Israel .) By this time, a single kingdom of Israel had formed throughout the country on both banks of the Jordan River , which over the next century became a major power of the Ancient East under the rule of the kings of Saul , David and Solomon .
In 930 BC e. the power of David and Solomon fell into two kingdoms, the northern kingdom became known as Israel , and the southern kingdom became Judea ( Heb. יְהוּדָה , Judah ). After the conquest of the kingdom of Israel by Assyria (722 BC), the name "Judea" gradually spread and became established as the name of the entire territory of the country.
Exiled by the Babylonians in 586 BC e., the Jews returned and around 520 BC. e. restored the Temple of Jerusalem , and then the independence of the country under the rule of the Hasmonean dynasty (167-37 years BC). The name “Judea” was also preserved under the rule of the Herodian dynasty (37 BC - 4 CE), imposed on the Jews by the Roman conquerors.
In the year 4 n. e. the Romans established their direct dominion in the country, proclaiming it a Roman province - the Province of Judea ( lat. Iudaea ).
The Roman emperor Hadrian crushed in 135 AD e. Jewish revolt against Rome led by Bar Kochba . He changed the name of Jerusalem to " Elijah Capitolina " and ordered the entire territory between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River to call Syria Palestinian - Lat. Syria Palaestina (Latin for the Greek name). The renaming was carried out in order to erase the memory of the kingdom of Judah [2] [11] . From the 4th century until the Arab conquest of the land of Syria, the Palestinian land, together with part of Sinai and part of the lands of the Nabatean kingdom , entered the Byzantine Empire as three provinces: Palestine Prima , Palestine Secunda , Palestine Terzia .
Since 638, the Arab conquerors called the country “Falastin” as the Arabic form of the name “Palestine”.
During the British mandate, the name "Palestine" was assigned to mandated territory. In the middle of the 20th century, the name " Palestinians ", formed from the word "Palestine", began to refer to the Arabs living in this territory ("Palestinian people", "Arab people of Palestine"), although before it defined all the inhabitants of the region and did not have ethnic coloring . [12] [13] [14]
Back in 1974, Syrian President Hafez al-Assad called Palestine "not only part of the" Arab homeland, "but also the main part of southern Syria" [15] .
In 1994, as a result of the Oslo Accords between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), the Palestinian National Authority (PNA) was formed to guide the territory of the West Bank and Gaza Strip . Currently, the PNA partially (along with Israel) controls only the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip is actually controlled by the Hamas movement, which is likely to plan to achieve independence of the Gaza Strip from the PNA [16] . The PNA seeks international recognition of the independence of the State of Palestine [17] , in connection with which the media often use the name “Palestine” [18] [19] [20] to refer to the Palestinian Authority and recognized by some countries [21] [22] [23] Palestine. Moreover, in the documents signed by Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization based on the Oslo Accords, the term Palestinian Authority is used [24] [25] [26] .
Palestinian Authority
Geography
The Palestine region is historically divided into the following geographical areas: Coastal plain (near the Mediterranean Sea ), Galilee (northern part), Samaria (central part, north of Jerusalem) and Judea (southern part, including Jerusalem), Zaordanie ( Transjordan ) - the eastern bank of the Jordan River . In particular, the Bible operates with these geographical concepts. Currently, the territory of Judea and Samaria in Russian-language sources is called the " West Bank ". Galilee, Samaria and Judea consist of a number of mountain groups, valleys and deserts .
The mountains in the south are the Judean Plateau, in the middle are the Samaria Mountains ( Grisim , Geval (Eyval)), then Tabor (Tavor; 562 m above sea level), Maly Hermon ( 515 m ), Carmel ( 551 m ), in the north - Hermon ( 2224 m ). In deep depressions significantly below sea level are Lake Tiberias (Lake Kineret; 212 m below sea level) and the Dead Sea , whose coast is the lowest land on Earth - at the end of 2015, the water surface was 430 m below sea level and continued to decline approximately 1 m per year .
History
Early History
In the 3rd millennium BC e. this territory called Canaan was inhabited by the Canaanite tribes.
In the XIII century. BC e. "the peoples of the sea" invaded the country from Crete and other islands of the Mediterranean Sea , attacking Egypt as well and gaining a foothold in the southern Mediterranean coast, in the area of the current Gaza Strip . From the neighboring seven-lingual peoples, they received the name plishtim , literally "invading", or the Philistines .
In the XI century BC e. the Hebrew tribes founded the kingdom of Israel , which disintegrated in 930 BC. e. into two: the kingdom of Israel (existed until 722 BC) and the kingdom of Judea (until 586 BC).
Antiquity
Subsequently, the region was conquered by the ancient Persian state of the Achaemenids, then it was part of the Hellenistic states of the Ptolemies and Seleucids (in the III – II centuries BC).
After the victory of the Maccabean revolt (167-140 BC), the Hasmonean kingdom (Judea) was created in it, and after the capture of Jerusalem by Pompey (63 BC), a territory called Judea became a vassal of Rome, retaining its the name also under the kingdom of Herod I from the Edomite dynasty. In the year 6 BC e. she came under the direct rule of Rome as the province of Judea , including Judea itself, Samaria , Galilee and Pereus ( Zaordanie )
After the defeat of the Bar Kochba rebellion against the Romans in 132 AD e., the Romans expelled a significant number of Jews from the country and renamed the province of Judea to “ Syria Palestine ” in order to erase the memory of the Jewish presence in these places forever [27] . The main Jewish population during this period moved from Judea to Galilee [28] .
In the years 395-614, Palestine was a province of Byzantium .
In 614, Palestine was conquered by Persia and became part of the Sassanid Empire .
After defeating Persia in 629, the Byzantine emperor Heraclius solemnly entered Jerusalem - Palestine again became a province of Byzantium .
The period of Arab rule (638-1099)
Around 636, at the very beginning of the Arab conquests , Palestine was conquered by Byzantium by Muslims [29] .
Over the next six centuries, control over this territory passed from the Umayyads [30] to the Abbasids , [31] to the Crusaders and vice versa.
The era of Arab rule in Palestine is divided into four periods:
- conquest and development of the country (638-660);
- Umayyad dynasty (661-750);
- dynasty of the Abbasids (750-969);
- Fatimid dynasty (969-1099).
Crusader Period (1099–1291)
In 1099, the Crusaders founded the Kingdom of Jerusalem here. However, already in 1187, Salah ad-Din ibn Ayyub took Jerusalem . But during the Third Crusade, the crusaders again returned to themselves Akkon ( Acre ), Ascalon ( Ashkelon ) and other cities. The Kingdom of Jerusalem was restored, although Jerusalem itself was in the hands of Muslims. The capital was Akkon.
In the summer of 1260, the Mongols invaded Palestine, but in the battle of Ain Jalut on September 3, 1260 they were defeated by Egyptian Muslims - the Mamelukes led by Kutuz and Beibars . This defeat blocked the Mongols' path to North Africa, and Egypt became the most powerful power in this region. Then the Mamluks began a war with the crusader states in Palestine. May 18, 1291 fell Akkon, May 19 - Tire . The fall of Sidon occurred in June, Beirut - July 31. Palestine was ruled by Egypt until the time of the Ottoman Empire .
Under the rule of the Ottoman Empire (1516-1917)
In 1517, the territory of Palestine was conquered by the Ottoman Turks under the leadership of Sultan Selim I (1512-1520). For 400 years, it remained part of the vast Ottoman Empire , covering a significant part of southeastern Europe, all of Asia Minor and the Middle East, Egypt and North Africa [32] .
In early 1799, Napoleon invaded Palestine. The French managed to capture Gaza , Ramla , Lod and Jaffa . The stubborn resistance of the Turks stopped the advance of the French army to the city of Acre , the English fleet came to the aid of the Turks. The French general Kleber managed to defeat the Turks at Kafr Cana and Mount Tavor (April 1799). However, due to the lack of heavy artillery, Napoleon was unable to seize the fortress of Acre and was forced to retreat to Egypt [27] .
In 1800, the population of Palestine did not exceed 300 thousand, 5 thousand of which were Jews (mainly Sephardim ). Most of the Jewish population was still concentrated in Jerusalem, Safed, Tiberias and Hebron. Christians, numbering about 25 thousand, were much more dispersed. The main places of concentration of the Christian population - in Jerusalem, Nazareth and Bethlehem - were controlled by the Orthodox and Catholic churches. The rest of the country's population was Muslim, almost all Sunnis [27] .
In the period 1800-1831, the country's territory was divided into two provinces ( vilayets ). The central-eastern mountainous region, stretching from Schema in the north to Hebron in the south (including Jerusalem), belonged to Damascus province ; Galilee and the coastal strip - to Akko vilayet. Most of the Negev was in this period outside of Ottoman jurisdiction [27] .
In 1832, the territory of Palestine was conquered by Ibrahim Pasha , the son and military leader of the Viceroy of Egypt, Muhammad Ali . His residence is located in Damascus. Palestine, the northern border of which reached Sidon , became a single province. The Egyptians, who ruled the country for eight years (1832-1840), carried out some reforms along the European lines, which provoked resistance from Arabs and uprisings in most cities of the country, which were crushed by force. During the period of Egyptian domination, extensive research was conducted in the field of biblical geography and archeology. In 1838, the Egyptian government allowed England to open a consulate in Jerusalem (previously consulates of the European powers existed only in the port cities of Acre, Haifa and Jaffa, as well as in Ramla). After 20 years, all major Western countries, including the United States , had consular missions in Jerusalem [27] .
In the 19th century, Jerusalem again became the most important Jewish center of Eretz Yisrael . Safed, who vied with Jerusalem for spiritual primacy, was badly damaged by the earthquake (1837), which claimed the lives of about 2 thousand Jews, and fell into decay.
In 1841, Palestine and Syria returned under the direct control of Turkey. By this time, the Jewish population of Palestine had doubled, while the Christian and Muslim population remained unchanged [27] .
In 1847, the head of the Catholic Church, Pope Pius IX restored the Latin Jerusalem Patriarchate [33] .
By 1880, the Palestinian population reached 450 thousand people (according to the Turkish census of the settled population, a little more than 270 thousand people), [34] of which 24 thousand were Jews. Most Jews in the country still lived in four cities: Jerusalem (where Jews made up more than half of the total 25,000th population), Safed (4,000), Tiberias (2,500) and Hebron (800), as well as in Jaffa (1 thousand) and Haifa (300). Jerusalem became the largest city in the country [27] . The flow of aliyah increased after the opening of the shipping line between Odessa and Jaffa [27] .
From the end of the 19th century, a large-scale settlement of Palestine by Jews , followers of the ideology of Zionism, began .
The first big wave of modern Jewish immigration, known as the First Aliyah ( Hebrew עלייה ), began in 1881, when Jews were forced to flee the pogroms in Eastern Europe [35] .
В начале XX века население составляло приблизительно 450 тысяч арабов и 50 тысяч евреев. [36]
Вторая алия (1904—1914 годы) началась после Кишинёвского погрома . Приблизительно 40 тысяч евреев поселилось в Палестине [35] .
28 марта 1917 года во время приближения британской армии (противника Османской империи в Первой мировой войне ) к Яффо , всем жителям города было предписано его покинуть, два дня спустя такое же объявление появилось в Тель-Авиве. Остаться было разрешено только феллахам (в связи со сбором урожая) и землевладельцам. За исполнением приказа евреями власти следили значительно строже, чем за исполнением его арабами. 1 апреля Джамаль-паша объявил, что все должны покинуть город в течение 8 суток из-за опасений, что он может быть разрушен до основания. 8 мая агентство «Рейтер» передавало, что Джамаль-паша угрожал евреям судьбой турецких армян [37] .
Британский мандат
В результате Первой мировой войны в апреле 1920 года на конференции в Сан-Ремо Великобритания добилась мандата на управление территорией Палестины (утверждён Лигой Наций в июле 1922 года). Английская подмандатная территория Палестина включала в себя также территорию, ныне занимаемую Иорданией. 2 ноября 1917 года английское правительство опубликовало декларацию Бальфура , в которой содержалось обещание содействовать созданию в Палестине «национального очага для еврейского народа». Однако в феврале 1922 года Уинстон Черчилль , министр колоний Великобритании, бывший противником реализации принципов декларации Бальфура, принял решение отдать ¾ территории мандата под отдельный эмират Трансиордания , из которого впоследствии (в 1946 году) было образовано независимое королевство Трансиордания [38] .
В 1919—1923 годах ( Третья алия ) в Палестину прибыли 40 тысяч евреев, в основном из Восточной Европы. Поселенцы этой волны были обучены сельскому хозяйству и могли развивать экономику. Несмотря на квоту иммиграции, установленную британскими властями, еврейское население выросло к концу этого периода до 90 тысяч . Болота Изреэльской долины и долины Хефер были осушены, и земля сделана пригодной для сельского хозяйства.
В то время страну населяли преимущественно арабы-мусульмане, однако самый крупный город, Иерусалим, был преимущественно еврейским [39] .
Из-за Яффских бунтов в самом начале Мандата Британия ограничила еврейскую иммиграцию, и часть территории, планировавшаяся для еврейского государства, была отдана под образование Трансиордании [40] , на территории которой было запрещено селиться евреям [41] .
В 1924—1929 годах ( Четвёртая алия ) в Палестину приехали 82 тысячи евреев, в основном в результате всплеска антисемитизма в Польше и Венгрии . Впоследствии, однако, приблизительно 23 тысячи эмигрантов этой волны покинули страну.
Подъём нацистской идеологии в 1930-х годах в Германии привёл к Пятой алии , которая была наплывом четверти миллиона евреев, спасавшихся от Гитлера . Этот наплыв закончился Арабским восстанием 1936—1939 годов и изданием Британией «Белой книги» в 1939 году, которая фактически сводила на нет иммиграцию евреев в Палестину.
По окончании Второй мировой войны еврейское население Палестины составляло 33 % по сравнению с 11 % в 1922 году [42] [43] .
Последующие события
В 1947 году британское правительство отказалось от мандата на Палестину, аргументируя это тем, что оно не способно найти приемлемое решение для арабов и евреев [44] .
29 ноября 1947 года Организация Объединённых Наций приняла план раздела Палестины (резолюция Генеральной ассамблеи ООН № 181). Этот план предполагал разделение Палестины на два государства — арабское и еврейское. Иерусалим был объявлен международным городом под управлением ООН, чтобы не допустить конфликта по его статусу.
« Ишув » (евреи, проживающие в Израиле) принял этот план [45] , но Лига арабских государств и Высший арабский комитет подмандатной Палестины его отвергли [46] .
In December 1947, the High Commissioner of Palestine submitted to the Ministry of Colonial Affairs a forecast that the territory allocated for the creation of an Arab state would be divided as a result of the alleged war between Syria (eastern Galilee ), Transjordan ( Samaria and Judea ) and Egypt (southern part) ) [15] .
The creation of Israel
On May 14, 1948, the formation of the state of Israel was proclaimed in the former Mandate of Palestine [47] .
The next day, seven Arab states ( Egypt , Syria , Lebanon , Transjordan , Saudi Arabia , Iraq, and Yemen ) attacked a new country, thereby starting the First Arab-Israeli War [47] [48] .
After a year of hostilities, a ceasefire was declared and temporary boundaries were identified, called the Green Line . Transjordan annexed what later became known as the West Bank and East Jerusalem , and the Gaza Strip remained under Egyptian control.
The Arab state was not created in the former Mandate Territory.
In 1967, during the Six Day War, the entire territory of the mandated Palestine was under Israeli control (78% of the mandated territory was given to the Arabs by the Arabs - the so-called Zayordan Palestine, part to the Saudi tribes, part to Syria).
The struggle to create an Arab state in the 1960s – 2010s
The question of creating an Arab state in the former Mandate of Palestine was practically removed from the agenda until the mid-1960s. The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), created in 1964, and its allies did not recognize the creation of the state of Israel and waged war against it. The Arab countries adopted a decision at the Khartoum summit in August 1967, called “three no”: no peace with Israel, no recognition of Israel and no negotiations with him [49] , and supported the PLO.
The situation began to change in the late 1980s and early 1990s after the conclusion of a peace treaty between Israel and Egypt and the related negotiations between Israel and Jordan .
In 1993, after the preparation of the decisions of the Oslo Accords, the PLO officially recognized the UN Security Council Resolutions 242 and 338 and officially announced its rejection of the desire to destroy Israel and the methods of terror, Israel recognized the PLO as a negotiating partner [50] [51] . As a result of these negotiations, the Palestinian National Authority was established in 1994.
On November 29, 2012, following a vote in the UN General Assembly ( 138 votes in favor, 9 against, 41 abstained) the Assembly “granted Palestine the status of an observer state to the United Nations that is not a member of it, without prejudice to acquired the rights, privileges and role of the Palestine Liberation Organization in the United Nations as a representative of the Palestinian people in accordance with relevant resolutions and practices ” [52] [53] [54] .
The leaders of Israel’s leading political parties condemned the content of Mahmoud Abbas’s speech to the UN General Assembly, calling it “outrageous and distorting the story” (opposition leader Sheli Jahimovich ). Foreign Minister Avigdor Lieberman said that “a speech full of slander only confirms the fact that while Abu Mazen is at the head of the Palestinians, he will not bring any progress to his people, but will use it to satisfy personal interests. “Abu Mazen will bring only unnecessary suffering to the Palestinians, making it impossible for a peaceful settlement.” The Office of the Prime Minister of Israel stated that “we are talking about a meaningless step that will not entail any changes” [55] .
Earlier, Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said that “a Palestinian state will not be created without Palestinians recognizing Israel’s right to exist as a Jewish state, it will not be created without Israel’s guarantees of completion of the conflict, and it will not be created without ensuring the complete security of our country.” " [56] .
Israel responded to the recognition of Palestine as an expansion of settlements. [57]
The dispute over the historical right to Palestine
The question of the historical right to Palestine between Palestinian Arabs and Jews is a matter of intense debate.
Some authors claim that Palestinians are descendants of the ancient pre-Jewish population of Canaan. . This opinion is shared by the far- left Israeli politician and journalist Uri Avneri [58] .
Other sources suggest that, unlike the disappeared Canaanites and Philistines, the Jewish presence in Palestine was never interrupted [59] [60] [61] .
Russian presence in Palestine
Russian Palestine is the collective name of land holdings and real estate belonging to the Russian Empire , and then the USSR in the Middle East in the 19th-20th centuries. The Russian Empire, and in particular the Russian Orthodox Church, managed to make significant acquisitions and even create an entire infrastructure designed to receive pilgrims from Russia and other Orthodox countries . It was sold to Israel by the Soviet Union as a result of the so-called “ orange deal ” in the 1960s.
Negotiations are ongoing on the return of the Russian Compound of Russia. [62]
Notes
- ↑ 1 2 Origins of the Name “Palestine”
- ↑ 1 2 3 Israel. Land of Israel (Eretz Yisrael). Geographical sketch - an article from the Electronic Jewish Encyclopedia
- ↑ Instructions for the transfer on maps of the geographical names of Arab countries. - M .: Nauka, 1966 .-- S. 26.
- ↑ Palestine Definition
- ↑ The non-Semitic people invading Canaan, most likely from the island of Crete .
- ↑ Philistines - article from the Electronic Jewish Encyclopedia
- ↑ History of Herodotus Book of Second Eutherpus (Unavailable link) . Date of treatment August 1, 2011. Archived on March 8, 2016.
- ↑ Strabo Geography, Book XVI. (p. 755-765 according to Kazobon)
- ↑ Pliny the Elder , Natural History , Vol. 5, XIII. 66
- ↑ Diodorus of Sicily , History, Book XIX, Ch. 93
- ↑ Bernard Lewis, “The Middle East: A Brief History of the Last 2,000 Years” Scribner | 1995 | ISBN 0-684-80712-2 | 465 pages, p. 31
- ↑ Netanyahu B. Place in the Sun, Chapter 4
- ↑ Boris Shustef. Palestinian Sharon // Jewish World, May 24, 2002.
- ↑ The Palestinian Identity (link unavailable) . Date of treatment October 30, 2010. Archived on August 9, 2011.
- ↑ 1 2 Arab Imperialism: The Tragedy of the Middle East, Efraim Karsh (link not available) . Date of treatment November 6, 2010. Archived on August 7, 2011.
- ↑ Gaza Strip prepares for secession - Kommersant, 07/24/2012
- ↑ Abbas submitted to the UN an application for recognition of Palestine // Lenta.Ru, 09/23/2011
- ↑ Russian Newspaper, plot / section “Palestine and Israel”
- ↑ Palestine admitted to UNESCO - News. Ru, 10/31/2011
- ↑ International Criminal Court rejected Palestine's lawsuit against Israel - Lenta.Ru, 04/04/2012
- ↑ Icelandic Parliament recognizes Palestinian independence - Lenta.Ru, 12/15/2011
- ↑ Thailand recognized Palestinian independence - Lenta.Ru, 01/20/2012
- ↑ Chilean government recognized Palestinian independence - Lenta.Ru, 01/07/2011
- ↑ Declaration of Principles, September 13, 1993
- ↑ Agreement on the Gaza Strip and the Jericho Area, May 4, 1994
- ↑ Agreement on Preparatory Transfer of Powers and Responsibilities, August 29, 1994
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Israel. Land of Israel (Eretz Yisrael). Historical Essay - an article from the Electronic Jewish Encyclopedia
- ↑ Palestine: History (inaccessible link) . The Online Encyclopedia of the Roman Provinces . The University of South Dakota (02.22-2007). Date of treatment July 5, 2007. Archived June 21, 2000.
- ↑ Ancient Palestine . Microsoft (2007). Date of appeal September 30, 2007.
- ↑ Palestine: The Rise of Islam (English) (2007). Date of appeal September 19, 2007.
- ↑ Palestine: 'Abbasid rule (English) (2007). Date of appeal September 19, 2007.
- ↑ Palestine: The Crusades (English) (2007). Date of appeal September 19, 2007.
- ↑ Hanna Kildani. Modern Christianity in the Holy Land: Development of the Structure of Churches and the Growth of Christian Institutions in Jordan and Palestine . - AuthorHouse, 2010 .-- P. 280. - 740 p. - ISBN 1449052851 .
- ↑ Palestine // Encyclopaedia Britannica . - 9th ed. - Edinburgh: Adam and Charles Black, 1885 .-- T. XVIII. - P. 178.
- ↑ 1 2 Immigration . Jewish Virtual Library . The American-Israeli Cooperative Enterprise. Released July 12, 2007. The source provides information on the First, Second, Third, Fourth, and Fifth Aliyot in their respective articles. The White Paper leading to Aliyah Bet is discussed here .
- ↑ Lubarsky G.A. 1900. Palestine: Her present and future (inaccessible link)
- ↑ Mordechai Naor. Exile
- ↑ Winston Churchill and Zionism: A Throwing History Stanislav Kozheurov, Ivan Fadeev, Alec D. Epstein, Lechaim November 2009
- ↑ JVW Shaw, “A Survey of Palestine, Vol 1: Prepared in December 1945 and January 1946 for the Information of the Anglo-American Committee of Inquiry”, Reprinted 1991 by The Institute for Palestine Studies, Washington, DC, p. 148 ( English)
- ↑ Liebreich, 2005 , p. 34
- ↑ State of Israel. Israel and the Palestinian issue - an article from the Electronic Jewish Encyclopedia
- ↑ The Population of Palestine Prior to 1948 . MidEastWeb. Date of treatment July 5, 2008.
- ↑ Population Statistics " . English - Palestinian ProCon.org. Date accessed July 7, 2008.
- ↑ Background Paper No. 47 (ST / DPI / SER.A / 47) . United Nations (April 20, 1949). Date of treatment July 31, 2007. Archived May 24, 2008.
- ↑ History: Foreign Domination . Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs (October 1, 2006). Date of treatment July 6, 2007.
- ↑ Bregman, 2002 , p. 40–1
- ↑ 1 2 Part 3: Partition, War and Independence . The Mideast: A Century of Conflict . National Public Radio (October 2, 2002). Date of treatment July 13, 2007.
- ↑ War of Independence - article from the Electronic Jewish Encyclopedia
- ↑ Abba Solomon Eban. Personal witness: Israel through my eyes . - Putnam, 1992 .-- P. 446. - 691 p. - ISBN 0399135898 .
- ↑ History of the Arab-Israeli conflict. Help Archived July 12, 2014. . jewish.in.ua.
- ↑ Kim Murphy. Israel and PLO, in Historic Bid for Peace, Agree to Mutual Recognition . // Los Angeles Times . - September 10, 1993.
- ↑ The UN General Assembly, with 138 votes in favor, granted Palestine the status of an observer state to the UN that is not a member of it . UN (11.29.2012). Date of treatment November 30, 2012.
- ↑ UN General Assembly raised the status of the Palestinian Authority . Euronews, 11/29/2012.
- ↑ Palestine recognized by the UN observer state , RIA Novosti (November 30, 2012).
- ↑ The reaction of Israeli leaders to the UN decision on the recognition of Arab Palestine . newsru.co.il (November 30, 2012). Date of treatment December 2, 2012.
- ↑ Netanyahu announced the conditions for the creation of a Palestinian state . cursorinfo.co.il (November 29, 2012). Date of treatment December 2, 2012. Archived December 4, 2012.
- ↑ Israel responded to Palestine’s recognition of expansion of settlements // lenta.ru
- ↑ Avneri W. So whose is Acre?
- ↑ Continuous Jewish Presence in the “Holy Land,” by Joseph E. Katz Source: “From Time Immemorial” by Joan Peters, 1984
- ↑ Shmuel Katz. Land of discord. Jewish presence in Eretz Yisrael
- ↑ Goitein Sh. D. Jews and Arabs - Their Relations Through the Ages // Chapter 6. Economic Transformation and Community Reorganization of the Jewish People in Islamic Times
- ↑ Russia will buy from Israel the Russian Compound in Jerusalem / Orthodoxy. Ru
Literature
- Gusterin P.V . : Cities of the Arab East, 2007
- Gusterin P.N. A. Mednikov and his role in the history of Arabic studies // Orthodox Palestinian collection. - Vol. 107.- M., 2011.
- Jewish cultures: a new look at history: Sat. / Ed. David Beale. - Moscow: Knizhniki, 2013 .-- 352 p. - Series "History of the Jews." - ISBN 978-5-7516-1131-1
- Tsirkin Yu.B. History of Bible Countries // AST LLC, Astrel, Transitbook, 2003, Classical Thought Series, p. 576. (English)
- EWG Masterman Dress and Personal Adornment in Modern Palestine // The Biblical World, Vol. 18, No. 3 (Sep., 1901), pp. 167-175. (eng.)
- Bregman, Ahron (2002), A History of Israel , Palgrave Macmillan, ISBN 0333676319
- Liebreich, Fritz (2005), Britain's Naval and Political Reaction to the Illegal Immigration of Jews to Palestine, 1945-1948 , Routledge, ISBN 0714656372
Links
- Palestine // Biblical Encyclopedia of Archimandrite Nicephorus . - M. , 1891-1892.
- Turaev B.A. Palestine // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron : 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - SPb. , 1890-1907.
- Palestine in the Open Directory Project Link Directory (dmoz)
- Articles on the history of Palestine: II millennium BC e. and I millennium BC. e . The World History. Encyclopedia. Volume 1. (1956)
- Palestine in the Ottoman Empire
- Arabs once recognized Israel