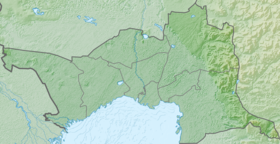
The state natural reserve "Akzhayik" ( Kazakh. "Aқzhayyk" memlekettik table reserve ) is located in Makhambet district of Atyrau region and the lands of the city of Atyrau .
| Reserve "Akzhayik" | |
|---|---|
| kaz "Ақжайық" reserves | |
| IUCN Category VI (Sustainable Environment Section) | |
| basic information | |
| Square | 111 500 ha |
| Founding date | February 6, 2009 |
| Managing Organization | Committee for Forestry and Fauna of the Ministry of Agriculture |
| Location | |
| A country |
|
| Region | Atyrau region |
| Areas | Makhambet district , Atyrau |
Established by Decree of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan No. 119 "On some issues of creating a state institution" State Natural Reserve "Akzhayik" dated February 6, 2009 in the Ural River delta and the adjacent coast of the Caspian Sea [1] .
On April 1, 2009, the territory of the Ural River delta and the adjacent coast of the Caspian Sea was included in the list of wetlands of international importance [2] . It became the second Kazakhstani territory after the Tengiz-Korgalzhyn lakes system, which was included in this list [3] .
In 2014, the reserve entered the UNESCO World Biosphere Reserve Network [4] .
Hydrology
The hydrological regime is characterized by a gradual rise in the water level in the Ural River in the second half of April, with a transition from May to June in the spring-summer flood, with a peak in late May or the first half of June. After the peak of the flood, first begins a rapid and then a gradual decrease in the level, passing in August — September into the autumn low flow period.
The depth of the lower reaches of the Ural River is stable due to the fact that every year the riverbed is washed with spring flood. In spring, during the flood, the water level exceeds the low-flow by 3–7 m. In the reach, the depths range from 7 to 20 m; the average depth of the Ural River along the fairway during low water is 3-5 m.
The Ural River belongs to typical rivers almost exclusively of snow feed. Its flow is mainly formed in the upper reaches, where the river network is well developed. Below Uralsk, before flowing into the sea, the Ural River has no tributaries, except the low-flowing Barbastau River. The annual flow of the river ranges from extremely low-water - 2 cubic kilometers per year, to full-flowing - 12 cubic kilometers per year. The water content of the river depends on the intensity of snow melting and the water supply of the upper reaches of the Ural River.
Since 1978, the level of the Caspian Sea began to rise sharply. The intensity of the sea level rise averaged 14 cm / year, in some years it reached 30 cm / year.
Extensive shallow waters, small slopes of the seabed and land, the configuration of the sea coastline, and wind activity create the conditions for the development of significant surge pressure fluctuations. Here, on average, 3-4 surges and 4-5 shoots are observed per month. One of the main features of hydrological and morphological processes off the coast of the Caspian Sea is that this process occurs in conditions of significant changes in sea level. Under moderate wind conditions, the coastline is 3-5 km, in extreme conditions - when sgone, the value of drying can reach 8-12 km, and the amount of land inundation in certain coastal areas - up to 20-30 km. The duration of surges varies from several hours to several days.
In the northern Caspian, the seasonality of the largest surge is clearly traced. Surges in the fall (October-November, 25.1%) have the highest frequency, in summer (June-July, 21.3%) and in spring (April-May, 16.7%) during the passage of the seamen - long and strong winds of the surge direction .
Climate
The climate of the North Caspian region is sharply continental and extremely dry with long hot and dry summer, with dust storms drying out the soil, short with frequent thaws, little snow and windy winter, with little and unstable precipitation. The average annual rainfall is 150 mm (ranges from 50 to 300 mm). The average annual wind speed is 5.5-7 m / s. Relative air humidity in summer does not exceed 37%, in winter - 80–84%. Precipitation is low - from 150 to 190 mm per year. Characterized by strong winds, dust storms. Wind speed of 5-6 m / s, rarely - up to 12 m / s. Storms occur on average 20-30 days a year.
Flora and fauna
According to recent studies, the list of flora includes 130 species belonging to 90 genera, 33 families, which is approximately 54% of the flora of the Kazakh part of the Northern Caspian region, which has about 250 species. Here you can find rare and listed in the Red Book of Kazakhstan plants.
The vegetation of aquatic or aquatic ecosystems is divided into 2 main types: submerged-aquatic , or phytobenthos - communities dominated by large algae attached to the bottom of the submerged water column and higher aquatic plants; air-water - communities dominated by higher plants - hygrophytes in the upper, surface tier ( reed , thorn , etc.), including those floating on the surface ( water lilies , water chestnut , etc.) and the submarine tier ( eagle-leaf , urut , etc. ).
The Siberian-East-African migratory route of migratory birds passes through the territory of the Ural river delta and the adjacent coast of the Caspian Sea. A large number of rare and endemic (living only in a given area) plant and animal species are concentrated here.
Of the birds, these are rare species such as the hatchback , the spoonbill , the little white heron , the Egyptian heron , the sultan . During the flight, thousands of flamingos , curly pelicans , black-headed laughter , swans , and also the endangered goose-bird stop here.
78 mammal species are found on the reserve.
In the list of endangered species in the region there are 20 types of birds, 24 species of insects, 2 species of reptiles and 2 species of mammals. On the verge of destruction - sturgeon fish and the Caspian seal .
Notes
- ↑ Site of the UNDP / GEF Project “Integrated Conservation of Priority Globally Important Wetlands as Habitats of Migratory Birds: A Demonstration in Three Territories”. The territory of the Korgalzhyn nature reserve has been expanded and a new reserve “Akzhaiyk” has been created in the Ural river delta (inaccessible reference is history ) . The appeal date is August 21, 2009.
- ↑ Site of the UNDP / GEF Project “Integrated Conservation of Priority Globally Important Wetlands as Habitats of Migratory Birds: A Demonstration in Three Territories”. The territory of the delta of the Ural River and the adjacent coast of the Caspian Sea is included in the List of Natural Zones Protected by the Ramsar Convention (Inaccessible reference is history ) . The appeal date is August 21, 2009.
- ↑ The official website of the Ramsar Convention. The Annotated Ramsar List: Kazakhstan (English) . The appeal date is August 21, 2009.
- ↑ Two Kazakhstani natural parks were included in the UNESCO list of specially protected heritage sites . Today.kz. Archived July 2, 2014.