The Parc National du Banc d'Arguin National Park, Banc d' Argen [1], located in Mauritania on the Atlantic coast between Nouakchott and Nouadhibou , includes sand dunes , coastal swamps , small islands and shallow waters. Since 1989, it has been included in the UNESCO World Heritage List due to the valuable natural complexes of the transition zone between the desert and the ocean . The park is replete with migratory birds that fly here for the winter. Several species of sea turtles and dolphins also live [2] .
| Bank d'Argen | |
|---|---|
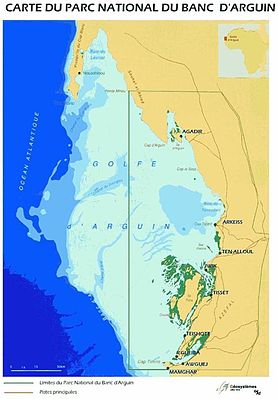 Map of Bank d'Argen National Park | |
| IUCN Category II ( National Park ) | |
| basic information | |
| Square | |
| Established | |
| Location | |
| A country |
|
| Banc d'arguin national park | |
| Link | No. 506 on the World Heritage List |
| Criteria | ix, x |
| Region | Africa |
| Turning on | 1989 ( 13th session ) |
Content
History
On June 24, 1976, Decree No. 74 176 / P / G created Bank d'Argen National Park, which became Africa's largest coastal park. In 1982, according to the Ramsar Convention, the object was given international importance. In 1986, the NGO Fondation Internationale du Banc d'Arguin (FIBA) was established . In 1986, the reserve included Bei do Levri and Las Quevesillas . In January 2000, a law was passed restricting any non-traditional activities in the park [3] .
Geographical characteristics
The area of the park is 1,200,000 ha, of which 55% is maritime territory, 45% is land. The absolute height varies from 5 m below sea level to 5 m above sea level.
The park is an example of a transition zone between the Sahara desert and the Atlantic Ocean . It is a 300 km long gulf with a coastline of sand dunes, wetlands, mangrove swamps, labyrinths of canals and bays , small islands and sandbanks. The bay includes Ile de Tidra - the largest island measuring 8 by 35 km - and 14 islands measuring more than 1 km in width and 5 km in length. The prevailing trade winds between Cape Blank and Timiris formed sandy bays from the coastline. The coast is low, the excess of the highest coast over the lowest is only 5 m [3] .
The coast is located on the border of temperate and tropical climatic zones. There is a large temperature contrast between the humid coastal air cooled by ocean water and the desert temperatures of the mainland . The prevailing northeastern trade winds from the Sahara and northwestern trade winds over the ocean strongly affect the climate of the area. Wind speeds of more than 8 m / s are noted. Precipitation is not regular, averaging 34–40 mm per year. Due to the high evaporation, the salinity of the water increases with approaching the coast. The cold season is in January – May with a minimum temperature in December (8 ° C), the warm season is in August – October with a maximum in September (34 ° C) [3] .
Flora
The park is located on the border of the afrotropic and palearctic biogeographic zones. Vegetation of 600-800 km² of shallow water includes Zostera noltei , Cymodocea nodosa and Halodule wrightii . They are sludge hardeners, produce oxygen and are a refuge for a large number of invertebrates , which provide the best forage base for fish in West Africa . The vegetation of the salt coasts and islands is salt-loving and includes Sesuvium portulocastrum , Salsola baryosma , Salicornia senegalensis , Suaeda fruticosa and others. White mangrove swamps from Avicennia africana occupy 1400 ha on the coast of Ile de Tidre and 1700 ha in the bay near Cape Timiris. They are the northernmost mangroves in the eastern Atlantic [3] .
Bogs from Spartina maritima , Ipomoea pes-caprae and Sporobolus virginicus are observed behind the mangroves. The mainland vegetation is Sahara with a little Mediterranean. Stipagrostis pungens , Cornulaca monacantha , Euphorbia balsamifera and Calligonum comosum grow on sand dunes. There are trees - Acacia raddiana , Balanites aegyptiaca , Maerua crassifolia and Capparis decidua ; herbaceous plants - Panicum turgidum , Cassia italica , Pergularia tomentosa and Heliotropium bacciferum [3] .
Fauna
The coast contains a large amount of marine phytoplankton , which creates an energy base for many birds and fish. There are thousands of crabs ( lat. Uca tangeri ), lat. Cardium edule and gastropods. Of the approximately seven million charadriiformes using the Atlantic route , approximately 30% winter in Bank d'Argen, which is their largest population in the world. The number of breeding fish-eating birds is 15 species. At least 249 bird species from the afrotropic and paleoarctic biogeographic zones were recorded [3] .
Mammals include about 20 gazelle dorcas ( lat. Gazella dorcas ), mainly on the Ile de Tidre, jackals ( lat. Canis aureus ), lat. Fennecus zerda , sand fox ( lat.Vulpes rueppelli ), sand dune ( lat. Felis margarita ), African wild cat ( lat. Felis lybica ), genetta ( lat. Genetta genetta ), African striped marten ( lat. Poecilogale albinucha ), honey badger ( lat. Mellivora capensis ), striped hyena ( lat. Hyaena hyaena ). The park contains a population of the rarest monk seals ( lat. Monachus monachus ) that inhabit Cape Blanc. Of marine mammals, there are West African dolphins ( lat. Sousa teuszii ), common dolphins ( lat. Delphinus delphis ), lat. Steno bredanensis , bottlenose dolphin ( Latin Tursiops truncatus ), gray dolphin ( Latin Grampus griseus ) and killer whale ( Latin Orcinus orca ). Finwal ( lat. Balaenoptera physalus ) and porpoise ( lat. Phocoena phocoena ) were also noted [3] .
Notes
- ↑ Geographic Encyclopedic Dictionary: Geographic Names / Ed. A.F. Treshnikov . - 2nd ed., Additional .. - M .: Soviet Encyclopedia , 1989. - P. 56. - 592 p. - ISBN 5-85270-057-6 .
- ↑ Unesco. Banc d'Arguin National Park . Date of treatment December 7, 2008. Archived March 22, 2012.
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 UNEP-WCMC. Banc d'Arguin National Park (inaccessible link) . Date of treatment December 7, 2008. Archived on September 30, 2007.