Ficus rubbery , or Ficus elastic ( lat. Ficus elastica ) - a species of plants from the genus Ficus ( Ficus ) of the family Mulberry ( Moraceae ).
| Ficus rubbery | |||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Scientific classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| International scientific name | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Ficus elastica roxb. ex hornem. , 1819 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
The native land of the plant is northeast India ( Assam ) and south Indonesia ( Sumatra and Java ).
Content
Description
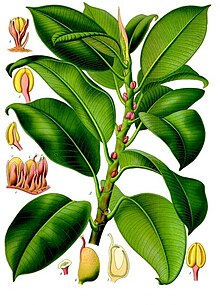
Rubber ficus is an evergreen tree reaching a height of 30-40 meters.
The leaves are alternate, oval with a sharp end, leathery, shiny, up to 20-30 cm in length and 10-20 in width. Young leaves have a pinkish-brownish color, old ones are dark green.
Fruits are small, yellow-green, oval in shape, reaching a diameter of 1 cm.
Application
Ficus rubber is of industrial importance as a tree producing rubber .
Outside the tropics, the plant is grown as a decorative indoor .
The most famous decorative varieties:
- Ficus elastica 'Decora' - with bronze young leaves;
- Ficus elastica 'Doescheri' - with variegated leaves.
In India it is used for growing "live" suspension bridges .
General form | Branches with leaves | Leaves | Fruit | Aerial roots |
Notes
- ↑ For the conventionality of specifying the class of dicotyledons as a superior taxon for the plant group described in this article, see the APG Systems section of the Dicotyledonous article .
Literature
- Botany. Encyclopedia "All plants of the world": Per. from English = Botanica / ed. D. Grigoriev et al. - M .: Könemann, 2006 .-- S. 374-375. - ISBN 3-8331-1621-8 .