

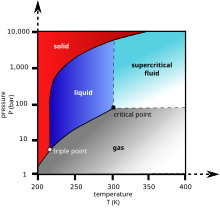
“Dry ice” is solid carbon dioxide CO 2 , under ordinary conditions ( atmospheric pressure and room temperature ), transforming into a gaseous state, bypassing the liquid phase .
In appearance it resembles ice (hence the name). The sublimation temperature at normal pressure is 194.65 K ( -78.5 ° C ). Technical “dry ice” has a density of about 1561 kg / m³ , and when sublimated it absorbs about 590 kJ / kg ( 140 kcal / kg ) of heat.
It is developed on carbon dioxide installations . It is used mainly for cooling food products (for example, ice cream ) during their transportation and storage, in research work to obtain low temperatures, during testing and assembly of some units in mechanical engineering, etc.
GOST 12162-77 : Dry ice (carbon dioxide) is a low-temperature product obtained from liquid or gaseous carbon dioxide . Non toxic White colour.