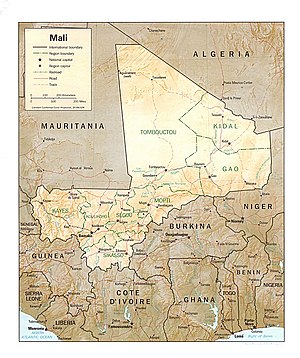
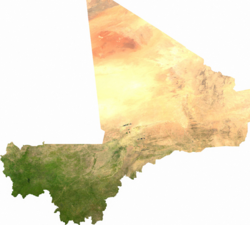


The state of Mali is located in West Africa .
Area: total - 1,240,292 km² (surface area - 20,000 km²). The length of the borders with Algeria is 1376 km, Burkina Faso - 1000 km, Guinea - 858 km, Côte d'Ivoire - 532 km, Mauritania - 2237 km, Niger - 821 km, Senegal - 419 km.
Content
- 1 Relief and rivers
- 2 Climate
- 3 Geology and minerals
- 4 Ecology
- 5 Links
Relief and rivers
The territory of the country can be divided into 3 main geographical regions: the rather fertile Western Sudan (in the south), the arid Sahel (in the central regions) and the desert region of the Sahara (in the north).
The northeast of the country is occupied by low mountains and hills (up to 1000 m), the southern part of Mali is represented by savannah. Deserts and semi-deserts occupy up to 65% of the country. The highest point in Mali is Mount Gombori Tondo (1155 m); the lowest point is the level of the Senegal River (20 m).
The largest rivers of the country are Niger and Senegal . Niger flows through the country from the border with Guinea to the border with Niger, over 1693 km, here it forms a large inland delta, creating a fertile region. Niger is of crucial economic and transport importance to Mali.
Climate
The climate of the country as a whole is characterized as tropical and rather arid, changing from north to south. In Bamako (south-west of the country, at an altitude of 340 m), a hot climate is characteristic, the average annual rainfall is 1120 mm, temperatures usually vary from 16 to 30 ° C, reaching 46-47 ° C. The rainy season in Bamako lasts from May to September, the dry season - from December to February. The average annual rainfall in Gao (Sahel region) is 220 mm, in Timbuktu - only 183 mm.
Geology and Minerals
Geologically, the territory of Mali is formed by two main forms: the West African platform (in the west) and the Tuareg shield (in the southeast). The vast plains are formed mainly by granite and clay shales, covered with sandstone and alluvial quartz.
There are reserves of bauxite, copper, diamonds, gold, gypsum, iron ore, limestone, phosphates, silver, uranium, zinc and other minerals. However, far from all deposits are developed, some of them are not economically significant. The potential of hydropower is also quite large.
Ecology
For Mali, environmental issues such as desertification , deforestation , soil erosion , drought are relevant.