Kupuasu , or Theobroma grandiflora ( lat. Theobroma grandiflorum ) is a fruit tree from the genus Theobroma of the Byttnerioideae family of the Malvaceae family ( Malvaceae ) (previously, the genus belongs to sterculievim ). A close relative (and partly analogous) of cocoa .
| Cupuasu |
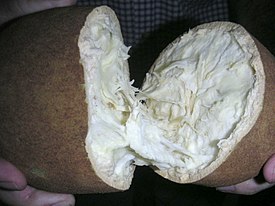
Cupuasu fruit |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
| The kingdom : | Green plants |
| Subfamily : | Byttnerioideae |
|
| International Scientific Name |
|---|
Theobroma grandiflorum ( Willd. Ex Spreng. ) K.Schum. 1886 |
|
Content
Homeland plants - forests of Amazonia . Kupuas was cultivated in South America in the pre-Columbian era; it is currently cultivated mainly in northern Brazil ( Pará , Amazonas , Rondônia , Acre and Maranhão states), and also introduced into the humid tropics of Venezuela , Colombia , Ecuador , Peru , Costa Rica and Mexico .
Kupuasu is a tree with a height of 5–15 m (wild plants can reach heights of up to 20 m) with brown bark.
The leaves are large leathery, bright green velvety on top and gray below, 25-35 cm long and 6-10 cm wide. The flowers grow in bunches on the trunk and thick branches ( caulifloria ), they are pollinated by insects, mainly aphids and ants. Fruits are oblong, juicy, fragrant, up to 25 cm long and up to 12 cm wide, with a dense red-brown peel 4-7 mm thick.
Inside the fruit contains white soft sourish-sweet flesh with 25-50 seeds, located in five nests. The flesh has a unique flavor and contains theacin purine alkaloid (unlike cocoa , which contains caffeine , theobromine and theophylline ). It is used fresh and is used to make juices , sweets, jams , liqueurs , yogurts , added to ice cream and various drinks.
Seeds, which occupy one fifth of the volume of the fruit, contain up to 50% of white oil, its properties close to cocoa butter, but having a higher melting point, so that chocolate (cupula) made from them does not melt in the mouth.
