Oenococcus oeni (lat.) - Gram - positive heteroenzymatic lactic acid cocciform bacteria of the genus Oenococcus . It takes part in the maturation of wines , fermenting malic and citric acid and forms diacetyl and other volatile aromatic substances, thereby lowering the acidity of the wine and giving the wine a pleasant aroma [1] . It used to be part of the Leuconostoc genus called Leuconostoc oenos , in 1995 it was proposed to transfer Leuconostoc oenos to the newly created genus Oenococcus Dicks et al. 1995 [2] .
| Oenococcus oeni |
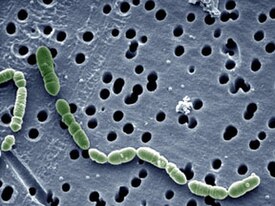
Oenococcus oeni , SEM (pseudocolor coloration) |
| Scientific classification |
|---|
|
| International scientific name |
|---|
Oenococcus oeni
( Garvie 1967) Dicks et al. 1995 |
| Synonyms |
|---|
- according to the NCBI website:
- Leuconostoc blayaisense
- Leuconostoc oeni corrig. Garvie 1967
- Leuconostoc oenos Garvie 1967
|
|
Oenococcus oeni is a gram-positive cocciform bacterium that forms chains. Energy is obtained as a result of heterofermentative lactic acid fermentation , the products of which are lactic acid , acetic acid and carbon dioxide . It can ferment various carbohydrates ( sucrose , fructose , glucose ) [3] , pyruvate [4] , as well as malic and citric acid. It forms proteases that remain active in the presence of sulfur dioxide and ethanol [5] . O. oeni is able to survive at an ethanol concentration of up to 10% in a nutrient medium.
In 1998, a genetic mapping of the genome of O. oeni strain PSU-1 was carried out and a physical map of the chromosome size of 1.857 Mp was constructed [6] . In 2006, the determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the DNA of the O. oeni genome of strain PSU-1 was completed. The genome is represented by a circular double-stranded DNA molecule of size 1780517 bp and contains 1864 genes , of which 1691 encode proteins , the percentage of% G + C pairs is 37%. The genome also contains several plasmids . Plasmid pOM1 is represented by a circular double-stranded DNA molecule of 3926 bp in size. and contains three genes, of which three genes encode proteins [7] . Plasmids pRS2 and pRS3 also carry three genes encoding proteins and are circular DNA molecules of 2544 and 3948 bp in size. respectively [8] [9] .
O. oeni takes on great importance in the process of wine ripening after the end of alcoholic fermentation [10] . O. oeni is responsible for malate-lactic acid fermentation processes [11] . In the process of life, O. oeni utilizes malic and lactic acids, thereby lowering the acidity of wine, and also produces diacetyl having a pleasant aroma, thereby improving the aroma of wine [12] . An important feature of O. oeni is its relative resistance to stress factors such as sulfur dioxide and copper ions, often present in wine [13] .
