Lipopolysaccharide binding protein ( LBP ) is a secreted protein , a component of the acute phase of inflammation that binds the bacterial lipopolysaccharide with high affinity and enhances its binding to CD14 . Thus, LSS provides the first step in the process of a monocytic immune response .
| Lipopolysaccharide Binding Protein | |
|---|---|
| Designations | |
| Characters | Lbp |
| Entrez gene | 3929 |
| Hgnc | 6517 |
| Omim | 151990 |
| Refseq | NM_004139 |
| Uniprot | P18428 |
| Other data | |
| Locus | 20th hr , 20q11.23 |
Structure
Lipopolysaccharide-binding protein consists of 456 amino acids , and the molecular weight is about 50 kDa. Contains 5 glycosylation sites .
Function
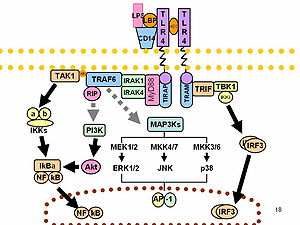
LSS is formed when gram-negative bacteria containing lipopolysaccharide are present in the higher organism. LSP has a high affinity lipopolysaccharide binding site. In addition, there is a CD14 binding site in the LSS. The resulting LPS / LSS complex then interacts with CD14 , which in turn activates the TLR4 receptor.