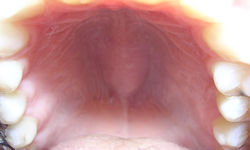
The palate ( Latin palatum ) is a horizontal septum separating the oral cavity with the nasal cavity and the nasal part of the pharynx , the common name for two anatomical formations - soft and hard palate. The palate is an integral part of the articulation apparatus .
| Sky | |
|---|---|
| lat palatum | |
 soft palate and hard palate SOFT PALATE HARD PALATE | |
 sky | |
| System | digestive (as part of the oral cavity) |
| Innervation | sensitive - maxillary nerve (branch of the trigeminal nerve) |
| Catalogs | |
Content
Anatomy
There are hard (front 2/3) and soft (back 1/3) palate.
Hard palate
The hard palate ( palatum durum ) - the bone wall that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity - is both the roof of the oral cavity and the bottom of the nasal cavity. In shape, a solid palate is a dome convex upward. In the anterior part it is formed by the palatine processes of the maxillary bones , in the posterior part by the horizontal plates of the palatine bones .
Soft palate
Soft palate ( palatum molle ) - a fold of the mucous membrane hanging over the base of the tongue (in the form of a palate curtain , lat. Velum palatinum ) and separating the oral cavity from the pharynx . The palatine curtain ends with a uvula .
The soft palate consists of two parts: connective tissue ( palatine aponeurosis ) and muscle, represented by the following muscles:
- The muscle straining the palatine curtain ( m. Tensor veli palatini ) - begins on the front of the temporal bone pyramid, goes forward and medially woven into the palatine aponeurosis.
- The muscle that lifts the palatine curtain ( m. Levator veli palatini ) - begins on the cartilaginous part of the auditory tube , goes down and is woven into the palatine aponeurosis.
- Muscles of the tongue ( mm. Uvulae ) - begin from the palatine aponeurosis, then are woven into each other, forming a palatine tongue.
- Palatine muscle ( m. Palatoglossus ).
- Palatine pharyngeal muscle ( m. Palatopharyngeus ).
Functions
- Together with other parts of the oral cavity, it is involved in the formation of certain sounds , in particular, posterior lingual and palatal consonants , palatalization , postalveolar, alveolo-palatine and uvular consonants .
- The transverse folds of the palate in humans are the rudiments of the palatal folds in animals , which are involved in grinding food .
- In some languages (e.g. German, English) historically appears as one of the organs of taste perception, as a result there are corresponding phrases / idiomatic expressions.
Development Anomalies
When the palatine processes are not fused, the so-called cleft palate is formed . In this case, the oral and nasal cavities are not isolated from each other. Mammals born with a cleft palate may soon die due to the inability to suck mother’s milk.
Literature
- The conceptual and terminological dictionary of a speech therapist / edited by V. I. Seliverstov . - M .: Humanitarian Publishing Center VLADOS , 1997. - 400 p. - 25 000 copies - ISBN 5-691-00044-6 .