Limonene - 1-methyl-4-isopropenylcyclohexene-1, a hydrocarbon of the terpenes group.
| D is Limonene and L is Limonen | |
|---|---|
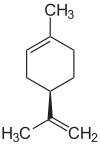 R-Limonen 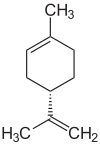 S-Limonen D - and L- limonene molecules | |
 | |
| General | |
| Systematic name | 1-methyl-4-isopropenylcyclohexene-1 |
| Traditional names | R-limonene and S-limonene, dipentene (for racemic mixture) |
| Chem. formula | C 10 H 16 |
| Physical properties | |
| condition | liquid |
| Molar mass | 136.24 g / mol |
| Density | 0.8411 g / cm³ |
| Thermal properties | |
| T. melt. | -74.25 ° C |
| T. bale. | 175.5-176.5 ° C |
| T. aux. | 42 ° C |
| T. ign. | 237 ° C |
| T. svpl. | 255 ° C |
| Steam pressure | 139.6 Pa (at 20 ° C) |
| Chemical properties | |
| Rotation [α] D | 87-102 ° |
| Optical properties | |
| Refractive index | 1.4720 for D- limonene 1.4717 for L- limonene (at 21 ° C) |
| Classification | |
| Reg. CAS number | 5989-27-5 |
| PubChem | |
| Reg. EINECS number | |
| Smiles | |
| Inchi | |
| RTECS | GW6360000 |
| Chebi | , and |
| ChemSpider | |
| Security | |
| LD 50 | 5 g / kg (rat, oral) |
Content
Sources and Application
It exists in the form of two optically active forms - enantiomers and in the form of a racemic mixture, which was previously considered one substance (dipentene). It is found in many essential oils (in citrus essential oils up to 90% D- limonene) and turpentine (4-6% dipentene in turpentine from Pinus silvestris common pine resin ).
D- limonene ( ( R ) - enantiomer ) has a citrus smell and is used as a perfume in perfumes and in the production of fragrances . The smell of L- limonene ( ( S ) -enantiomer) has a pronounced needles smell, this enantiomer is also used as a perfume. Its possible carcinogenic properties are discussed.
Chemical Properties
When heated to 300 ° C, the optically active forms of limonene racemize into dipentene, and at high temperatures (vapor transmission over a hot metal surface) decomposes to form isoprene .
Limonene is oxidized at the allylic position of the cyclohexene core to carvone , however, in industry, carvone is synthesized from limonene by nitrosation with nitrosyl chloride , followed by hydrolysis of the formed carvone oxime . Dehydrogenation of limonene in the presence of sulfur leads to the formation of zymol .
Biosynthesis
Limonene is formed from geranyl phosphate through the cyclization of an intermediate carbocation.
See also
- Carvon