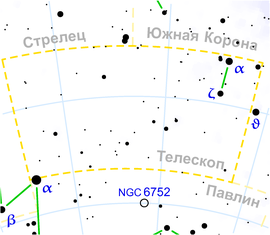
The telescope ( Latin Telescopium , Tel ) is the dim constellation of the southern hemisphere of the sky. It occupies an area of 251.5 square degrees in the sky, contains 50 stars visible to the naked eye.
| Telescope | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Lat. title | Telescopium (to the genus. n .: Telescopii ) |
| Abbreviation | Tel |
| Symbol | Telescope |
| Right ascension | from 18 h 00 m to 20 h 20 m |
| Declination | −57 ° to −45 ° 30 ′ |
| Square | 252 sq. M. degrees ( 57 place ) |
| The brightest stars ( value <3 m ) | not; the brightest |
| Meteor showers | not |
| Nearby constellations |
|
| The constellation is visible in latitudes from + 33 ° to −90 °. | |
Content
Observation conditions
The constellation in Russia is partially observed only in its southernmost regions, south of latitude + 44 ° 30 ′. The visibility period is extremely limited. Full visibility at latitudes south of + 33 °. Lies south of Sagittarius and the South Crown.
History
New constellation. Not related to legends. Introduced by Nicola Louis de Lacaille in 1756 , the Latin name was proposed in 1763 . Lacaille dedicated the constellation to a specific instrument - the Cassini air telescope .
Links
See also
Telescope constellation stars list