Iron gluconate - an iron preparation that makes up for the lack of iron in the body, restores hemoglobin . With a course of treatment, it contributes to the regression of the clinical and laboratory symptoms of anemia . Like iron fumarate , it is a highly absorbable and well-tolerated form of iron.
| Iron gluconate | |
|---|---|
| Ferrous gluconate | |
 | |
| Chemical compound | |
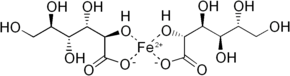
| IUPAC | Iron (II) D-gluconate (2: 1) dihydrate |
| Gross formula | C 12 H 24 FeO 14 |
| Cas | |
| PubChem | |
| Classification | |
| Farmakol. Group | Macro and microelements; Hematopoiesis stimulants |
| ATX | |
| ICD-10 | , and |
| Dosage Forms | |
| pills , syrup | |
| Route of administration | |
| Other names | |
| Iron Gluconate 300, Ferronal, Ferronal 35 | |
In the food industry it is registered as a food additive E579 as a color stabilizer. [one]
Content
Physical Properties
The powder is yellow-green or dark olive in color. Soluble in water. Insoluble in alcohol. Melting point 188 ° C.
Pharmacological action
Iron is an important trace element . It is part of hemoglobin, myoglobin and various enzymes . Iron stimulates the function of the blood-forming organs. Iron gluconate contributes to the rapid restoration of hemoglobin in patients with iron deficiency anemia.
Iron gluconate is better absorbed and absorbed than other forms of iron, due to its low ionization constant . It does not precipitate proteins , does not violate the proteolytic activity of the digestive system and does not cause nausea, stomach cramps, constipation or diarrhea in most patients.
Pharmacokinetics
Iron is absorbed mainly in the duodenum and upper jejunum . Iron gluconate is more easily absorbed than iron salts of inorganic origin. Absorption takes place the more intensively, the more pronounced deficiency of iron in the body. With a high content of calcium , phosphorus , phytic acid in the food, and secretory insufficiency of the stomach, absorption of iron is limited. In the blood, iron binds to transferrin protein and in the form of ferrotransferrin is delivered to the depot - bone marrow , liver , spleen , where it is deposited in the form of ferritin and hemosiderin . Iron is excreted mainly in urine and sweat , partially excreted by the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Indications for use
Prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemia caused by various causes: bleeding ( polymenorrhea , metrorrhagia , childbirth , hemorrhoids , peptic ulcer of the stomach and 12 duodenal ulcer , surgical interventions, frequent nosebleeds, blood loss in other diseases); increased need for iron ( pregnancy , lactation , intensive growth and donation , burns , hemodialysis ); insufficient intake of iron with food or impaired absorption (chronic diarrhea , achlorhydria , gastrectomy , celiac disease , Crohn's disease , enteritis , malabsorption syndrome ).
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity , hemochromatosis , hemosiderosis , late skin porphyria , chronic hemolysis , siderohrestichnoe anemia (including lead), thalassemia ; hemolytic (hereditary and acquired) and other anemia not associated with iron deficiency.
Caution
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, inflammatory bowel disease (enteritis, diverticulitis , ulcerative colitis , Crohn's disease), alcoholism (active or in remission), allergic diseases , bronchial asthma , hepatitis , liver or kidney failure , rheumatoid arthritis , transfusion blood .
Side
Allergic reactions (itching, hives ), nausea , vomiting , constipation or diarrhea , flushing of the skin, hyperthermia , dizziness , abdominal pain, toothache, chest pain , sore throat , back pain, gastralgia , irritability, staining of stool in dark color; with prolonged use - erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract .
Overdose
Symptoms: excessive fatigue or weakness, hyperthermia, paresthesia , pallor, cold clammy sweat, acrocyanosis , abdominal pain, vomiting and blood diarrhea, gastrointestinal mucosal necrosis, weak pulse , lethargy , low blood pressure , palpitations , convulsive seizures coma . Signs of peripheral circulatory collapse occur within 30 minutes after administration; metabolic acidosis, convulsions , fever, leukocytosis , coma - within 12-24 hours; acute renal and hepatic necrosis - after 2-4 days.
Treatment: it is necessary to rinse the stomach ; in case of severe poisoning, deferoxamine is administered intravenously slowly: for children - 15 mg / h, for adults - 5 mg / kg / h (up to 80 mg / kg / day); with mild intramuscular poisoning: children - 1 g every 4-6 hours, adults - 50 mg / kg (up to 4 g / day); symptomatic therapy. Hemodialysis is ineffective for excretion of iron, but can be used to accelerate the excretion of the Fe-deferoxamine complex, and can also be prescribed for oligo- or anuria . It is also possible to use peritoneal dialysis .
Dosage and administration
Inside, 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating, adults - 1.2-1.8 g / day in 2-3 doses; for prevention - 0.6 g / day in 2 doses; therapeutic dose for children - 0.3-0.9 g / day, prophylactic - 0.3 g / day. The duration of treatment should not exceed 6 months.
Special instructions
It is recommended to appoint premature infants from 2 months. Hepatic or renal failure increases the risk of cumulation of iron. May exacerbate ulcerative and inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis . To avoid the risk of erythremia , caution should be exercised during blood transfusion. To avoid accidental poisoning with iron, medicines should be kept out of the reach of children.
Interaction
Pharmaceutically incompatible with other drugs. A specific antidote is deferoxamine. Reduce absorption - antacid drugs, Ca 2+ drugs, ethidronic acid, coffee ; drugs that reduce the acidity of gastric juice (including cimetidine ; drugs containing carbonates , bicarbonates , phosphates , oxalates ), pancreatin , pancreolipase, milk , vegetables, cereals, egg yolk , tea - iron preparations should be taken 1 hour before or 2 hours after their use. Ascorbic acid enhances absorption. Reduces the absorption of fluoroquinolones , penicillamine , tetracyclines (they are recommended to be taken 2 hours before or 2 hours after taking iron preparations). Large doses of iron preparations reduce the intestinal absorption of Zn 2+ drugs (the latter are recommended to be taken 2 hours after taking iron preparations). Ethanol increases absorption and the risk of toxic complications.
Notes
- ↑ Archived copy (inaccessible link) . Date of treatment May 13, 2008. Archived April 21, 2008.